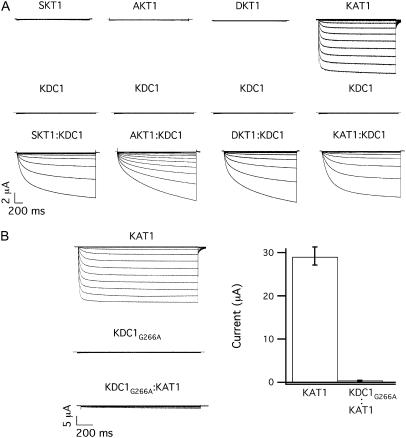
FIGURE 2.
KDC1 has strong affinity and modulatory capability when injected with other inward-rectifying subunits in Xenopus oocytes. (A) Typical ionic currents recorded after the injection of KDC1 (middle) or SKT1, AKT1, DKT1, and KAT1 (top from left to right) and by coinjection of KDC1 with the correspondent inward rectifying partner (bottom); data are representative of at least five experiments for each coinjections. (B) Glycine 266 was mutated into alanine in KDC1 pore and the mutated KDC1G266A was injected at a 1:1 weight ratio with wild-type KAT1. It can be observed that KDC1G266A strongly decreases the probability of occurrence of KAT1 homomers. Left typical currents, right mean currents ± SE of 12 experiments. Applied membrane potentials are from 0 mV to −240 mV in −20 mV steps; holding and tail potentials are 0 mV and −50 mV.