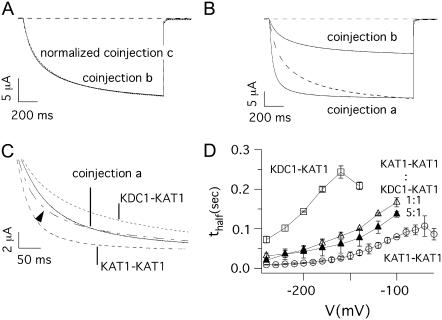
FIGURE 7.
Kinetics of currents mediated by different dimeric coinjections. (A) Normalized currents measured at V = −160 mV in oocytes coinjected with KAT1-KAT1 plus KDC1-KDC1 (coinjection b) and KDC1-KAT1 plus KDC1-KDC1 (coinjection c). (B) The current measured at V = −180 mV in an oocyte injected with KAT1-KAT1 plus KDC1-KDC1 (coinjection b) was normalized and superimposed (dashed line) with that measured at the corresponding voltage V = −150 mV in an oocyte injected with KAT1-KAT1 plus KDC1-KAT1 (coinjection a). For a fair analysis of the kinetics, we compared two currents taken at voltages shifted by ΔV ≈ 30 mV to take into account the voltage shift of the Boltzmann distributions of the two coinjections. (C) Current traces recorded at −150 mV from an oocyte coinjected with KAT1-KAT1 plus KDC1-KAT1 tandem constructs (coinjection a), and from two distinct oocytes injected with KAT1-KAT1 (V = −120 mV), and KDC1-KAT1 (V = −180 mV) tandem constructs, respectively. The dash-dotted line (indicated by the arrow) represents the linear combination of KAT1-KAT1 homomeric current (dashed line) and KDC1-KAT1 heteromeric current (dotted line) and is superimposed to that obtained by KAT1-KAT1 plus KDC1-KAT1 coinjection. (D) Half-activation times (mean ± SE, N ≥ 8) of ionic currents plotted as a function of the membrane voltage for KDC1-KAT1 (d1, open squares), KAT1-KAT1 (open circles) and coinjection a (KAT1-KAT1 plus KDC1-KAT1) at a cRNA ratio 1:1 (open triangles) and 5:1 (solid triangles).