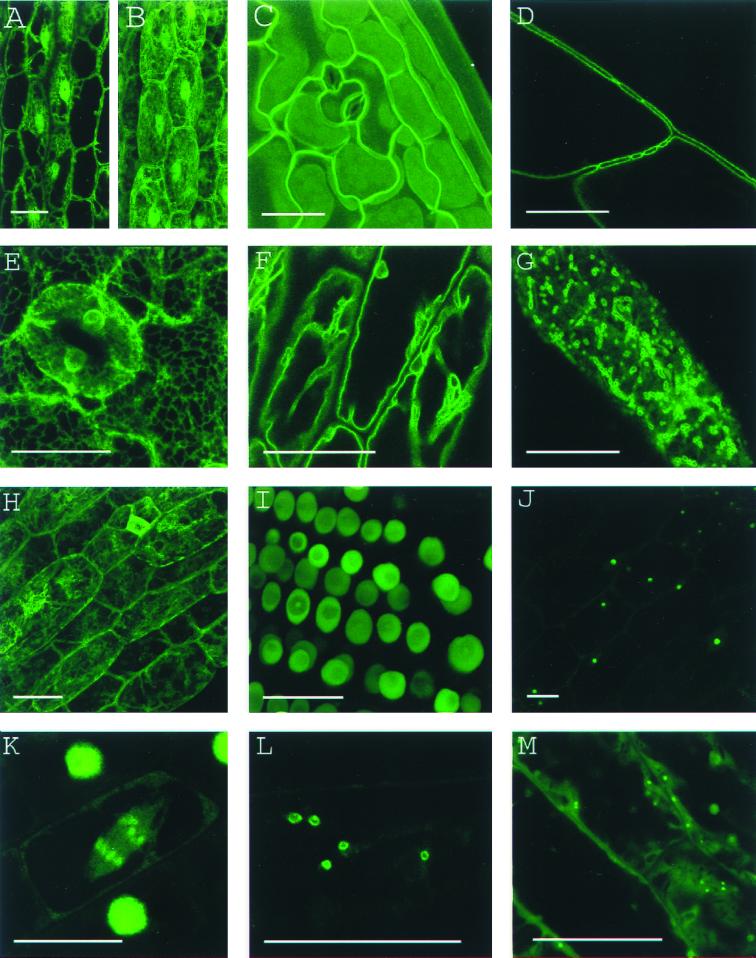
Figure 1.
Canonical images of marker classes. (A and B) Wild type: Hypocotyl epidermal cells of transgenic seedlings expressing pEGAD GFP; nuclei and cytoplasmic strands are evident. Shown for comparison are a single confocal optical section (A) and a brightest point projection of several optical sections (B) of the same plant cells. (C) Cell surface: Cotyledon epidermal cells of EGAD line Q8, which expresses a GFP fusion to the plasma membrane channel protein PIP2A. In plasmolysis experiments, GFP fluorescence associates with the membrane of plasmolysed cells, indicating the marker is not cell wall localized. (D) Cell contact junctions: Leaf petiole epidermal cells in line LEEZ, which expresses an out-of-frame fusion protein. Markers of this class highlight both plasma membranes and membrane contact zones. Contact zones are specific to the “cell contact junction group” and are not observed in members of the cell surface group. (E) Endoplasmic reticulum: Cotyledon epidermal cells in line Q4, which express an in-frame fusion to a predicted protein containing a carboxy terminal membrane anchor rich in lysine residues. This marker colocalizes with fluorescent BODIPY-Ceramide, an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane marker dye (data not shown), and is similar in appearance to KDEL-tagged GFP (20). (F) Vacuolar membrane: Hypocotyl epidermal cells in line Q5, which expresses a fusion to delta-TIP, a vacuolar membrane channel protein. Vacuolar membrane encasing trans-vacuolar cytosolic strands and invaginations creates a complicated pattern of fluorescence. The vacuolar membrane can be seen to flow over organelles at the cell periphery (see supplemental data) (G) Tiny bubbles: Hypocotyl epidermal cell of line Q10, which expresses a fusion protein to a novel glycine rich protein. In addition to the bubble-like structures, a reticulate ER-like pattern is also faintly marked in this line. The identity of the bubble-like structures is unknown but may be ER associated (see supplemental data). (H) Nuclear exclusion. Line Q1 expresses a fusion protein to a predicted small acidic ribosomal protein. Markers in this group do not show the nuclear localization characteristic of wild-type GFP (see B). (I) Nuclear: Root meristem cells in line N7, which expresses a GFP fusion to a transcription factor-like protein. (J) Nucleolar: Hypocotyl epidermal cells in line expressing a fusion protein targeted to the nucleus (K). Chromosomes: A dividing root cell in line M253, showing accumulation of the GFP∷CRY2 fusion protein on anaphase chromosomes. Before mitosis, the marker appears to localize to the nuclear lumen, as seen in several adjacent cells. These interphase nuclei are overexposed to better show the chromosomal pattern in the dividing cell. (L) Q-balls. Shown are structures of unknown identity illuminated by an out-of-frame fusion protein, F2. (M) Streaming dots: Hypocotyl cell of EGAD line V6, which expresses a fusion to an EST of unknown function. The images shown in B–E and G–I are brightest-point projections of confocal Z-series. The remaining images are single optical sections acquired by using confocal microscopy. (Bars = 20 μm.)