Figure 4.
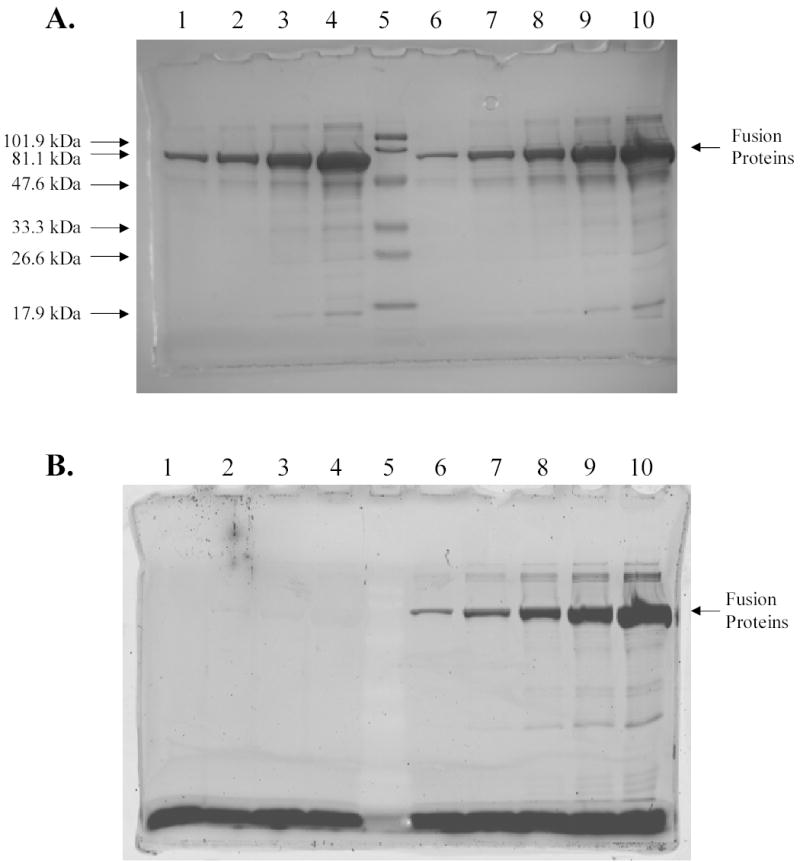
Analysis of fusion proteins between cytoplasmic MBP and R-PE apo-alpha subunit by SDS-PAGE. A, Detection of proteins by Coomassie staining. B, Detection of proteins by fluorescence imaging (excitation wavelength 532 nm; emission filter 580BP30). Lanes 1–4, the fourth, the third, the second, and the first purification fractions of MBP-R-PE alpha subunit fusions without PEB; lane 5, prestained MW standards, low range 18–106 kDa (Bio-Rad); lane 6–10, the fifth, the fourth, the third, the second, and the first purification fractions of MBP-R-PE alpha subunit fusions with PEB. Results show that MBP-R-PE fusion protein with molecular weight of ~ 65 kDa was successfully purified under native conditions. Fusion proteins isolated from cells incubated with PEB were fluorescent in contrast to fusion proteins isolated from cells that were not incubated with PEB. The highest amount of fusion proteins was found in the first elution fractions. The same conclusions were obtained after isolation of cytoplasmic MBP-R-PE beta subunit fusions.
