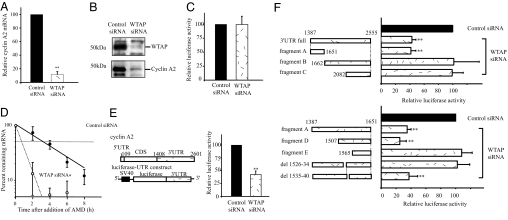
Fig. 2.
WTAP knockdown leads to the reduction of cyclin A2 mRNA and protein levels because of destabilization of cyclin A2 mRNA. (A) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of cyclin A2 expression. Cyclin A2 mRNA levels were decreased to 10% that of controls 24 h after siRNA transfection. Values are WTAP RNAi vs. control RNAi samples normalized to cyclophilin mRNA levels. (B) Western blot analysis of WTAP and cyclin A2. Cells were harvested 72 h after siRNA transfection. (C) The effect of WTAP knockdown on cyclin A2 promoter activity was studied by using a cyclin A2 promoter-luciferase reporter assay. The full promoter region of cyclin A2, corresponding to −737 to +108 bp (start site, +1), was inserted into the pGL3-basic plasmid. (D) Actinomycin D (AMD) was added at 24 h after siRNA transfection, and total RNA was prepared at each indicated time point. The remaining cyclin A2 mRNA was measured by quantitative real-time PCR and normalized to rpL32 mRNA, which has a half-life of >25 h. (E) Influence of the 3′UTR of cyclin A2 mRNA on WTAP-mediated mRNA stability. A luciferase-cyclin A2 3′UTR chimeric plasmid was constructed by subcloning in the 3′UTR fragment of cyclin A2 immediately downstream of the firefly luciferase ORF in a pGL3-control vector. At 12 h after siRNA transfection, HUVEC were transiently transfected with the chimeric luciferase-cyclin A2 3′UTR plasmid. Eighteen hours later, dual-luciferase assays were performed. Relative luciferase activity (firefly/Renilla) was normalized to the relative basal luciferase activity obtained from a pGL3-control vector. (F) Responsible region for WTAP-mediated mRNA stability was analyzed by using deletion constructs of cyclin A2 mRNA 3′UTR. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001 vs. control.