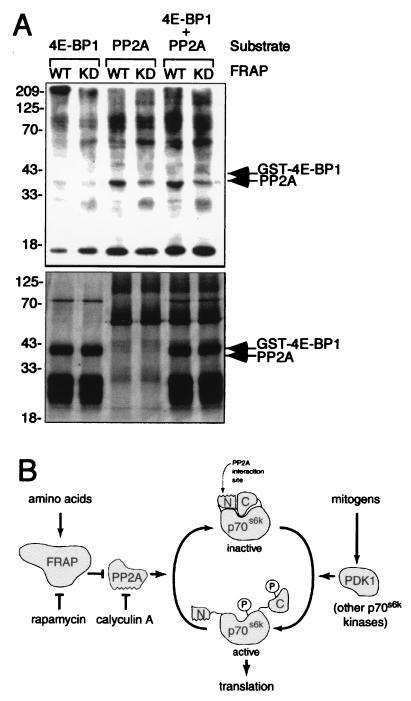
Figure 4.
Possible mechanisms of PP2A regulation by FRAP. (A) FRAP phosphorylates PP2A in vitro. Kinase-active (WT) and kinase-dead (DA) FRAP expressed in insect cells by baculovirus infection were immunoprecipitated and incubated with GST–4E-BP1 and/or PP2A as substrates in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. The products of the kinase reactions were separated by using SDS/PAGE before autoradiography (Upper). Relative quantities of kinase substrates were determined by silver staining (Lower). (B) A model of FRAP intervention in the p70s6k signaling pathway. Mitogenic stimuli promote phosphorylation of p70s6k which in turn promotes translation of a subset of cellular mRNAs. Inhibition of FRAP by amino acid deprivation or by rapamycin treatment interferes with p70s6k function by activating PP2A. PP2A dephosphorylates and inactivates p70s6k through its interaction with the N terminus of p70s6k.