Figure 1.
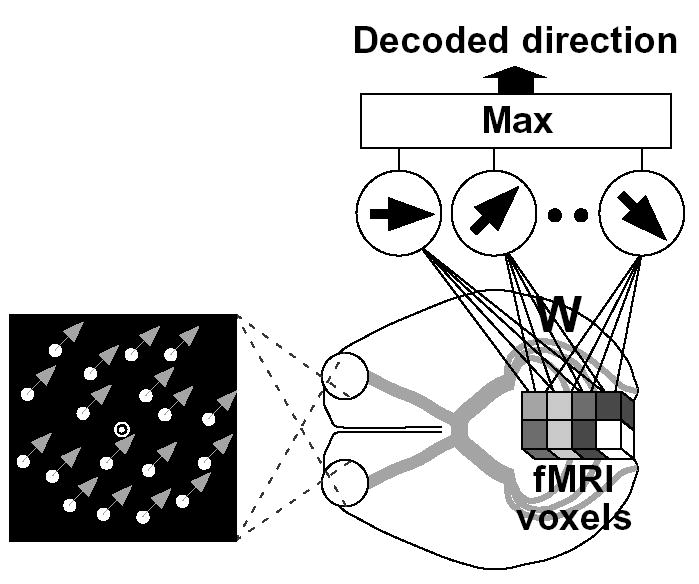
Decoding analysis of ensemble fMRI signals. An fMRI activity pattern (cubes) was analyzed by a “direction decoder” to predict the direction of moving dots seen by the subject. The decoder received fMRI voxel intensities, averaged for each 16-s stimulus block, as inputs. The next layer consisting of “linear ensemble direction detectors” calculated the weighed sum of voxel inputs. Voxel weights were optimized using a statistical learning algorithm applied to independent training data, so that each detector’s output became larger for its direction than for the others. The direction of the most active detector was used as the prediction of the decoder.
