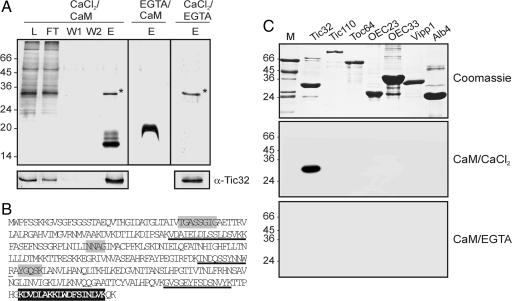
Fig. 1.
Identification of Tic32 as a calmodulin-binding protein. (A) Solubilized inner envelope membranes from pea chloroplasts were incubated with calmodulin-agarose in the presence (CaCl2/CaM and CaCl2/EGTA) and absence (EGTA/CaM) of calcium. L, load; FT, flow through; W, wash; E, eluate. With calcium, a single protein bound to the matrix that could be eluted either with calmodulin in the presence of CaCl2 (∗) or by EGTA alone (∗). The protein did not bind to the matrix in the presence of EGTA. The protein was identified as Tic32 by Western blot analysis (Lower) and by mass spectrometry (B). (B) Deduced amino acid sequence of Tic32 from Pisum sativum (AAS38575). Peptides obtained by mass spectroscopic analysis from the protein isolated in A are underlined. Black boxes indicate the calmodulin-binding site of Tic32. Gray boxes indicate conserved active side residues of SDRs. (C) A calmodulin-binding assay was performed by using a number of different heterologously expressed proteins with biotinylated calmodulin (Bottom). Interaction of Tic32 with calmodulin occurred in the presence of calcium but not with EGTA. M, protein marker; Tic32 and Tic110, components of the Tic translocon; Toc64, component of the Toc translocon; OEC23 and OEC33, components of the oxygen-evolving system; Vipp1, protein associated with the inner envelope; Alb4, integral thylakoid protein.