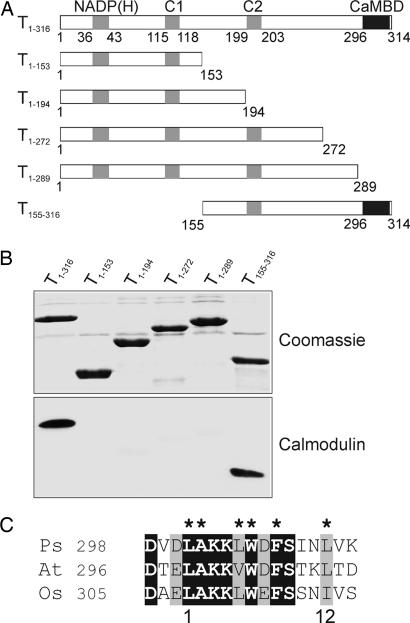
Fig. 2.
Identification of the calmodulin-binding domain of Tic32. (A) Schematic representation of Tic32 and various N- and C-terminal deletion constructs. The NADP(H) binding site as well as two regions identified in other SDRs as part of the active site (C1 and C2) are marked by gray boxes. The black box indicates the calmodulin-binding domain (CaMBD) identified in the experiment. Numbers indicate amino acid residues in correlation to the wild-type Tic32. (B) Equal amounts of heterologously expressed and purified proteins were analyzed for calmodulin binding by using biotinylated calmodulin (Lower). Removal of the 26 most C-proximal amino acids (T1–289) resulted in a loss of interaction between calmodulin and Tic32. (C) Alignment of the putative calmodulin-binding domain of Tic32 from pea (Ps; AAS38575) with the corresponding sequences of Tic32 from Arabidopsis thaliana (At; NP_849428), and Oryza sativa (Os; AAX96188). Identical residues in all sequences are boxed in black, whereas conserved residues are boxed in gray. Conserved hydrophobic residues within the sequence are marked by asterisks. A potential 1–12 motif for calmodulin binding is indicated below the sequences.