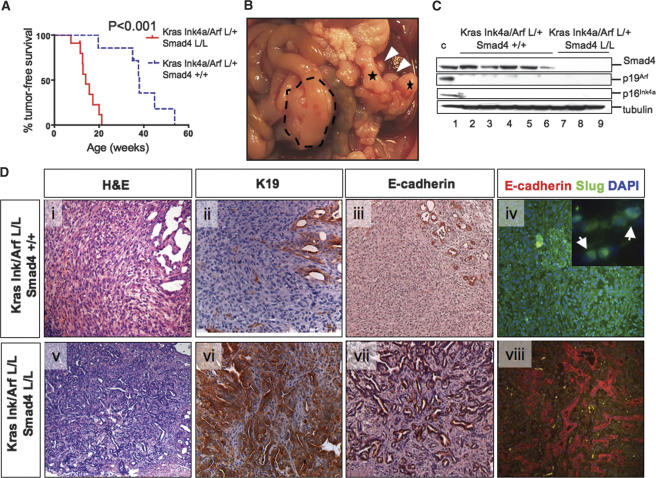
Figure 6.
Smad4 deletion promotes the glandular PDAC in cooperation with KrasG12D activation and Ink4a/Arf deficiency. (A) Kaplan-Meier analysis showing pancreas tumor-free survival of Ptf1a-Cre LSL-KrasG12D Ink4a/Arflox/+ Smad4lox/lox mice and Ptf1a-Cre LSL-KrasG12D Ink4a/Arflox/+ Smad4+/+ mice. Twelve of 13 deaths in the Ptf1a-Cre LSL-KrasG12D Ink4a/Arflox/+ Smad4lox/lox mice were due to PDAC, and one out of 13 was due to IPMN. (B) PDAC arising in a Ptf1a-Cre LSL-KrasG12D Ink4a/Arflox/+ Smad4lox/lox mouse (indicated by dashed line); note the liver metastases (white arrowheads). This mouse also showed an IPMN (denoted by asterisks). (C) Western blot analysis of lysates from early passage PDAC cell lines from the Ptf1a-Cre LSL-KrasG12D Ink4a/Arflox/+ Smad4+/+ (lanes 2–6) and Ptf1a-Cre LSL-KrasG12D Ink4a/Arflox/+ Smad4lox/lox (lanes 7–9) models for expression of Smad4, p19Arf, p16Ink4a, and tubulin. Lane 1 shows positive controls. (D) Undifferentiated PDAC from a Ptf1a-Cre LSL-KrasG12D Ink4a/Arflox/+ mouse (panels i–iv) and a moderately differentiated PDAC from a Ptf1a-Cre LSL-KrasG12D Ink4a/Arflox/+ Smad4lox/lox mouse (panels v–viii) stained with H&E (panels i,v), or with antibodies to cytokeratin-19 (panels ii,vi) and E-cadherin (panel iii,vii), and double-labeled with antibodies to E-cadherin (red) and Slug (green) (panels iv,viii). Magnifications: All are 100× except D (panel iv, inset), which is 630×.