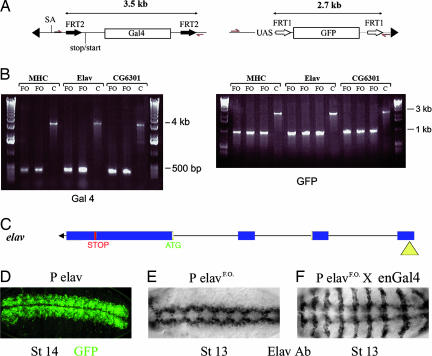
Fig. 2.
Postinsertion conversion to a misexpression construct. (A) Genomic DNA was isolated from various lines, and DNA fragments were amplified by PCR with primers indicated by red arrows in the diagram. Three insertions (in mhc, elav, and CG6301) were analyzed this way. (B) Fragments obtained by PCR. After excision (see lanes marked FO for flipped-out; two independent excisions), a 200-bp fragment was detected with the GAL4-specific primers, whereas a 3.5-kb fragment was produced in the parental flies. C, control; MHC, myosin heavy chain. Likewise, the flipped-out flies (three independent excisions) gave a 1-kb fragment with the GFP-specific primers, whereas a 2.7-kb fragment was obtained from the parental flies. (C) Diagram of the insertion site of the promoter trap (yellow triangle) in the 5′ end of the elav gene (transcription is from right to left). (D) GFP expression in the parental stock (promoter trap in elav). GFP is detected in the CNS as expected from a reporter of elav expression. (E) Immunocytochemical detection of Elav after FLP-mediated excision of GAL4 and GFP (PelavFO). (F) Elav expression in an embryo from a cross between engrailed-GAL4 and PelavFO. Note the expression in stripes in addition to the normal CNS expression.