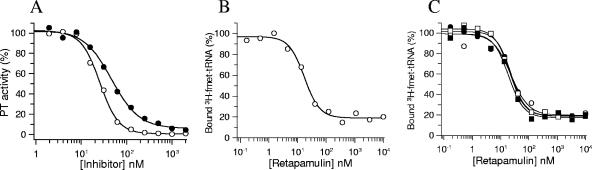
FIG. 5.
(A) Inhibition of ribosomal peptidyl transferase activity. Reaction mixtures containing ribosomes, [3H]fmet-tRNA, mRNA, and biotinylated puromycin were carried out in the presence of increasing concentrations of tiamulin (•) or retapamulin (○) as described in Materials and Methods, and the amount of [3H]fmet-biotin-puromycin was quantified using strepatividin SPA beads. IC50 determinations were made by fitting the data to a four-parameter IC50 equation. (B) Inhibition of fmet-tRNA binding to E. coli ribosomes. Ribosomes were incubated with [3H]fmet-tRNA (P-site substrate), tRNAphe (A-site substrate), mRNA, and increasing concentrations of retapamulin. The bound and free ligands were separated by filtration, and IC50 values were calculated. (C) Schild analysis of retapamulin displacement of fmet-tRNA binding. P-site binding reactions, as described above, were conducted by titrating retapamulin at 10 nM (▪), 20 nM (□), 60 nM (•), or 200 nM (○) concentrations of [3H]fmet-tRNA, and the bound ligand (%) was plotted as a function of the retapamulin concentration.