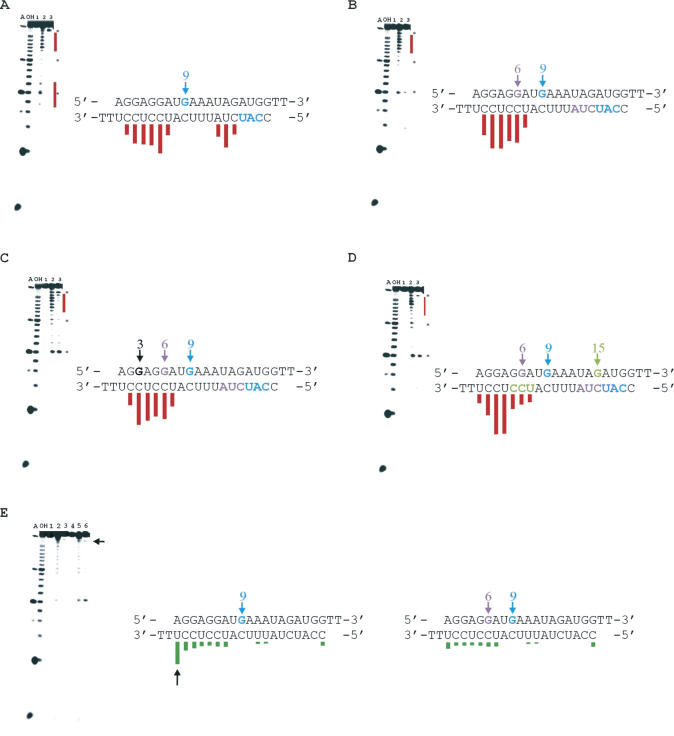
Figure 5.
Directed hydroxyl radical cleavage to probe PKR RBD binding of benzyl-modified siRNAs. (A–D) Directed hydroxyl radical cleavage by PKR RBD E29C-EDTA•Fe to probe PKR dsRBM I binding of benzyl-modified siRNAs. Conditions for A, OH, lane 1, lane 2 and lane 3 for (A–D) were identical to the conditions of A, OH, lane 1, lane 2 and lane 3 for Figure 3B. (A) Cleavage pattern on HPV-E7 siRNA benzylated at position 9 on the sense strand. (B) Cleavage pattern on HPV-E7 siRNA benzylated at positions 6 and 9 on the sense strand. (C) Cleavage pattern on HPV-E7 siRNA benzylated at positions 3, 6 and 9 on the sense strand. (D) Cleavage pattern on HPV-E7 siRNA benzylated at positions 6, 9 and 15 on the sense strand. (E) Directed hydroxyl radical cleavage by PKR RBD Q120C-EDTA•Fe to probe PKR dsRBM II binding of benzyl-modified siRNAs. A and OH were RNAse A and alkaline hydrolysis, respectively. Conditions for lane 1, HPV-E7 siRNA benzylated at position 9 with no added cleavage reagents (protein, hydrogen peroxide or sodium ascorbate); lane 2, same as lane 4 of Figure 3; lane 3, same as lane 5 for Figure 3; lane 4, HPV-E7 siRNA benzylated at position 6 and 9 with no added cleavage reagents; lane 5, same as lane 4 of Figure 3; lane 6, same as lane 5 for Figure 3. Asterisk indicates a hyper-reactive nucleotide showing cleavage independent of directed hydroxyl radical cleavage. The cleavage sites disrupted on the antisense strand are shown in the same color as the benzyl-modified nucleotide on the sense strand that causes the change.