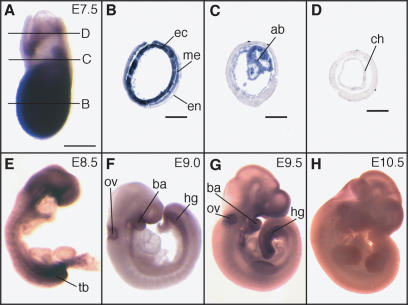
Figure 3.
Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis of ZFP206 expression during post-implantation mouse development. (A) At E7.5 ZFP206 is expressed throughout the embryo proper, the allantoic bud and weakly in the chorion. Anterior is to the left. (B–D) Transverse sections of the embryo as shown in (A). (B) In the embryo, proper ZFP206 is expressed strongly in the ectoderm (ec), moderately in the mesoderm (me) and there is weak to no expression in the endoderm (en). (C) ZFP206 is expressed in the allantoic bud (ab). (D) There is weak to no expression of ZFP206 in the extra-embryonic ectoderm, however, some expression was detected in the chorion (ch). (E–H) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of embryos at the labeled stages. (E) Widespread expression of ZFP206 throughout out the embryo at E8.5 with strong expression in the tail bud (tb) region. (F–G) At E9.0 and E9.5 expression is reduced but with persistent expression in the otic vesicle (ov), branchial arch (ba) and hindgut (hg). (H) Weak to no expression was detected at E10.5. Scale bars: (A) 200 μm; (B–D) 100 μm. Embryonic age was determined by the number of days after the formation of the copulation plug. Whole-mount in situ hybridizations were performed following a standard procedure with Digoxygenin-labeled ZFP206 antisense RNA probes.