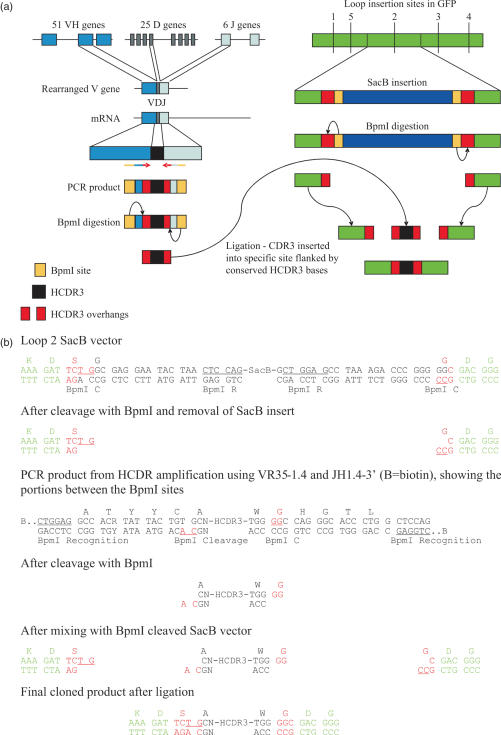
Figure 1.
(a) The genetic rearrangement which creates human VH genes, and the PCR strategy used to amplify, digest and purify HCDR3s is shown on the left, while on the right is shown the general scheme used to create a template for simple insertion of HCDR3s exploiting type IIs restriction sites and a negative selectable marker, such as SacB. (b) The detailed sequence of a recipient vector containing SacB inserted into loop 2, and the cloning strategy used to insert HCDR3s. The letters depicted in green represent GFP sequences, black are HCDR3 sequences, and red are junctional sequences which come together during the ligation procedure. As a result of the cloning procedure, the conserved cysteine present in the HCDR3 is converted into a serine. BpmI R (underlined) identifies the BpmI recognition site, while BpmI C identifies the cleavage site.