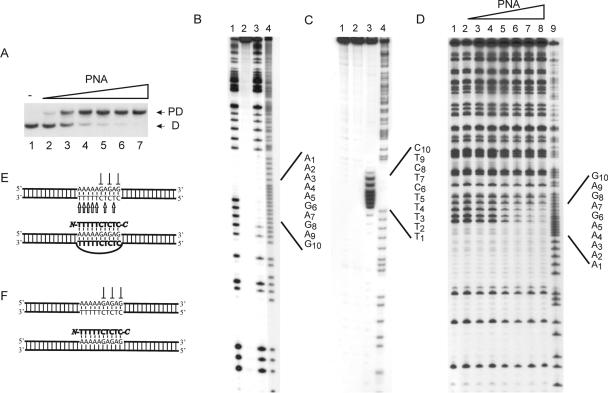
Figure 1.
P-loop formation on binding of PNA decamer to dsDNA: (PD10). (A) P-loop formation as investigated by gel-shift analysis. P-loops were generated using the following concentrations of PNA 1707: lane 1, w/o PNA; lane 2, 0.25 μM; lane 3, 0.5 μM; lane 4, 0.75 μM; lane 5, 1 μM; lane 6, 2 μM; and lane 7, 4 μM. P-loop (PD) and free dsDNA (D) are indicated. (B) In situ DMS probing of P-loop complex identified in (A): lane 1, dsDNA + DMS; lane 2, dsDNA w/o DMS; lane 3, PD10 + DMS; lane 4, A/G sequence. (C) In situ permanganate probing of P-loop complex identified in (A): lane 1, DNA + KMnO4; lane 2, DNA w/o KMnO4; lane 3, PD10 + KMnO4; and lane 4, A/G sequence. (D) DMS probing in solution at elevated high ionic strength (+90 mM KCl) and using the following PNA1707 concentrations: lane 1, w/o PNA; lane 2, 0.13 μM PNA; lane 3, 0.25 μM PNA; lane 4, 0.5 μM PNA; lane 5, 1 μM PNA; lane 6, 2 μM PNA; lane 7, 4 μM PNA; lane 8, 8 μM PNA; and lane 9, A/G sequence. (E) Structural assignment as based on the data in (A–C). (F) Structural assignment based on the data in (D and manuscript in preparation). We used the 168 bp XbaI–PvuII restriction fragment of p322 either 5′-kinase labeled (A and D) or 3′-Klenow labeled (C) with 32P-phosphate at the XbaI site. The 223 bp PvuII–EcoRI restriction fragment of p322 was 3′-Klenow labeled and used in (B). PNA incubations were at pH 6 as described in Materials and Methods.