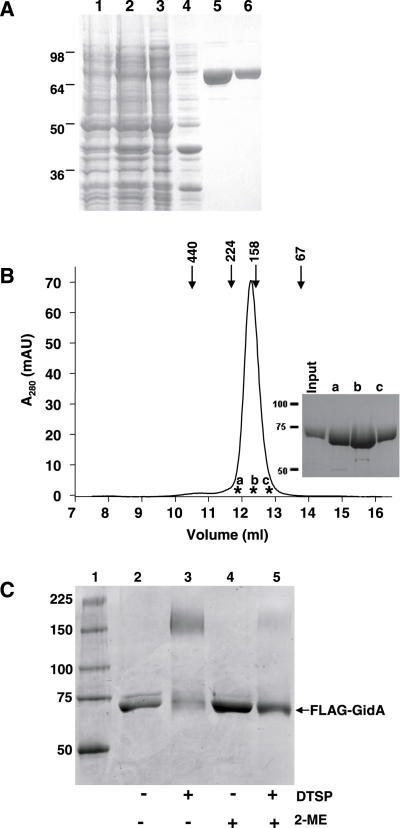
Figure 3.
Self-assembly of FLAG-GidA protein. (A) Purification of the recombinant protein FLAG-GidA. SDS–PAGE analysis of samples from different purification steps of the FLAG-GidA protein. The gel was stained with Coomassie blue. Lane 1, crude extract from uninduced DEV16/pIC1180; lane 2, crude extract from DEV16/pIC1180 induced with arabinose; lanes 3 and 4, cleared lysate (supernatant after sonication) and insoluble material (pellet after sonication) of the induced strain, respectively; lane 5, first eluate with elution buffer (containing free FLAG peptide); lane 6, second eluate with elution buffer. (B) Gel filtration analysis of purified FLAG-GidA. A total of 100 μg of FLAG-GidA were applied on a Superdex HR 200 column as described in Materials and Methods and 0.5 ml fractions collected. Markers indicate the positions of the standards: ferritin (440 kDa), β-amylase (224 kDa), aldolase (158 kDa), albumin (67 kDa). Inset: SDS–PAGE analysis of fractions indicated with asterisks in the chromatogram and designated as a, b, and c. (C) In vitro cross-linking of FLAG-GidA with DTSP. Protein samples, untreated or cross-linked with DTSP, were analysed by non-reducing SDS–PAGE. Lanes 4 and 5 show the effect of 2-ME on the reactions. Size of mass markers, run in lane 1, is indicated on the left in kDa.