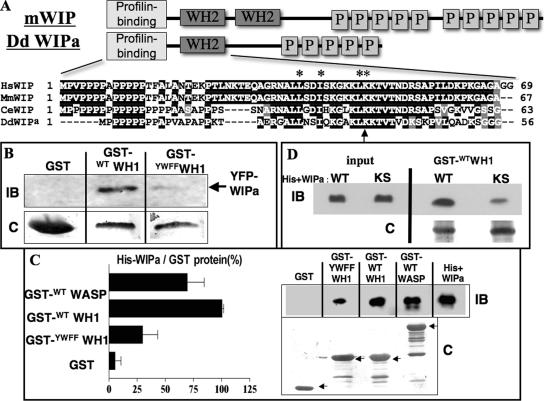
Figure 2.
DdWIPa is structurally and functionally similar to mammalian Wasp Interacting Protein (WIP). (A) Schematic representations of mammalian WIP and Dictyostelium WIPa. Sequence alignment of Wasp Homology 2 (WH2) domain shown with conserved residues in black. Residues essential for binding to G-actin are indicated with asterisks. Lysine 36 is indicated with an arrow. (B) YFP-WIPa was precipitated from AX3 cell lysates with either GST-fusion wild type or mutant WH1 bound to glutathione beads. Representative of three experiments is shown. IB, immunoblot; C, Coomassie staining. (C) Purified His-tagged WIPa was pulled down from solution using GST-WH1 or -WASP bound to beads. Representative of three experiments is shown. Each pulldown was quantitated and normalized to the quantity of GST-tagged protein used in the experiment. (D) Interaction between WH1 domain and WIPa depends partially on conserved residues K93 and S95 of WIPa. Purified His-tagged WT or mutant KS WIPa was pulled down from solution using GST-WH1. Three representative experiments are shown.