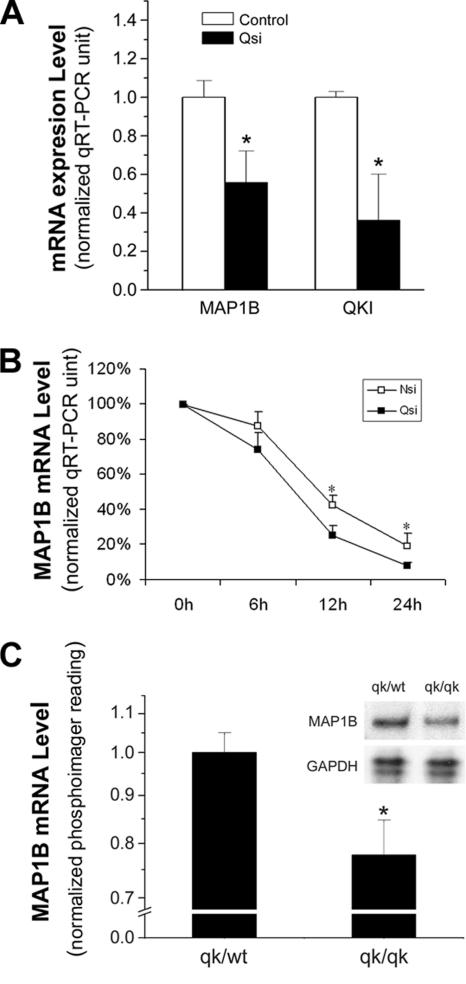
Figure 5.
QKI deficiency causes reduced expression of MAP1B in vitro and in vivo. (A) Knocking down QKI expression by siRNA significantly reduced MAP1B mRNA expression in CG4 cells. RNA extracted from QKI siRNA-treated cells and control siRNA-treated cells was used for qRT-PCR analysis of the mRNAs for QKI, MAP1B, and GAPDH. qRT-PCR reading for each sample was normalized to that of the GAPDH housekeeping mRNA, and results shown as the mean ± SD of four independent experiments are graphically displayed. (B) The decay of MAP1B mRNA in QKI siRNA- and control siRNA-treated CG4 cells. Twenty-four hours after siRNA-treatment, parallel cultures of cells were treated with actinomycin D to block transcription before isolating total RNA at the indicated time points of transcription inhibition. The qRT-PCR reading of MAP1B mRNA was normalized to that of the 18S rRNA before being plotted against time to generate the decay curve. (C) Reduced MAP1B mRNA expression in the qkv corpus callosum. RPA was performed using total RNA isolated from the dissected corpus callosum derived from qkv/qkv and the nonphenotypic qkv/wt littermate control. Inset, a representative RPA image of MAP1B and the loading control GAPDH. MAP1B mRNA level was quantitatively measured by a phosphorimager, normalized to the GAPDH signal and graphically displayed with SD (n = 5). * p < 0.05 by standard t test.