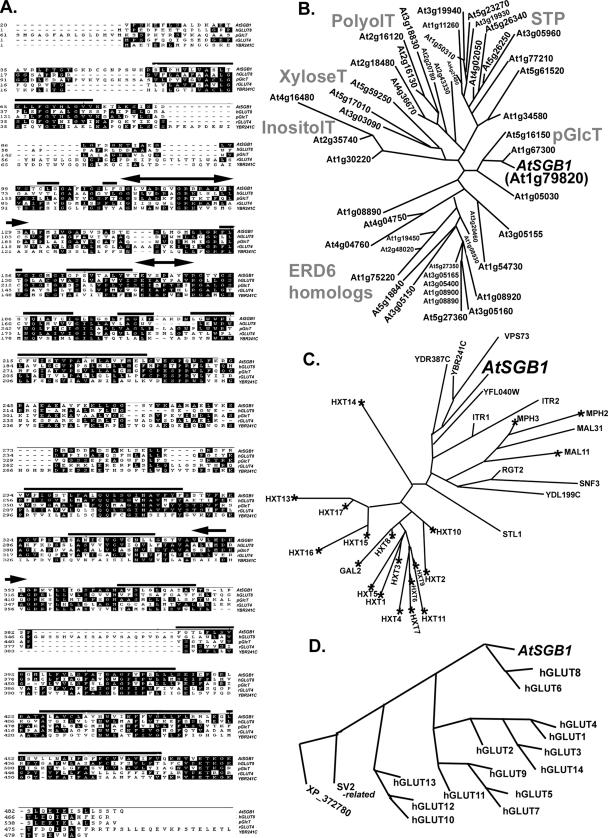
Figure 3.
The architecture of SGB1, a putative hexose transporter and a comparison to yeast and vertebrate homologues. (A) The SGB1 open reading frame encodes 495 amino acids. Partial sequences of SGB1 (At1g79820), a putative plastidic glucose transporter (pGlcT, At5g16150), and a rat glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4, NP_036883), and full-length sequences of human glucose transporter 8 (GLUT8, NP_055395 and an unknown protein from yeast (YBR241C) are aligned using DNA STAR Mega alignment. Regions of SGB1 with high probability to be membrane spanning are indicated by bold horizontal lines. A transmembrane domain hidden Markov model was used for transmembrane prediction. Sugar transporter signature 1 and 2 predicted for SGB1 are indicated by the double-headed arrows. The N-terminal extensions of SGB1 and pGlcT are truncated as is the C-terminal extension on rGLUT4 for space consideration. (B) SGB1 is a member of the monosaccharide transporter (-like) family. There are 49 proteins shown to be similar to SGB1 above a cut-off of 4 × 10−16 for Arabidopsis. These were analyzed cladistically as described in Materials and Methods. The family is composed of six clades of which functionality has either been determined experimentally for at least one submember or inferred bioinformatically. Arabidopsis SGB1 (designated in this figure as AtSGB1 for cross-genome comparison) is a member of a small group of plastidic glucose transporters. Although none of the Arabidopsis pGlcT have been shown experimentally to transport a monosaccharide, a pGlcT from spinach having high similarity to AtSGB1 has experimental proof (Weber et al., 2000). Other clades are designated accordingly (http://www.biologie.uni-erlangen.de/mpp/TPer/index_TP.shtml): STPs are sugar transpoters. ERD6 homologues are the early responsive to dehydration stress proteins. PolyolT, XyloseT, and InositolT are transporters of polyol, xylose, and inositol transporters, respectively. (C) Among 31 expressed yeast hexose transporters and glucose sensors having sequence identity to AtSGB1 (cut-off E value = 4.8 × 10−10), AtSGB1 is most similar to a subgroup of proteins with unknown function. The largest group is the hexose transporter family of S. cerevisiae, composed of 18 proteins (Hxt1–17, Gal2). These proteins and other three maltose transporters (MPH2, MPH3, and MAL11) are essential for metabolic glucose consumption. RGT2 and SNF3 are glucose sensors that generate an intracellular signal inducing expression of glucose transporter (HXT) genes (Ozcan and Johnston, 1999). A hexose transport deficient strain (EBY.VW4000) was generated through deletions in the 21 genes marked with an asterisk and used for genetic complementation by SGB1. Accession numbers for the yeast homologues are provided in the following Web site with GBS1 protein sequence as a query: http://seq.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/nph-blast2sgd. (D) Comparison of Arabidopsis SGB1-16 human hexose transporters. The E value cut-off for selecting the vertebrate sequences was 8 × 10−11. Accession numbers for the human homologues are provided in the following Web site with GBS1 protein sequence as a query: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/Blast.cgi.