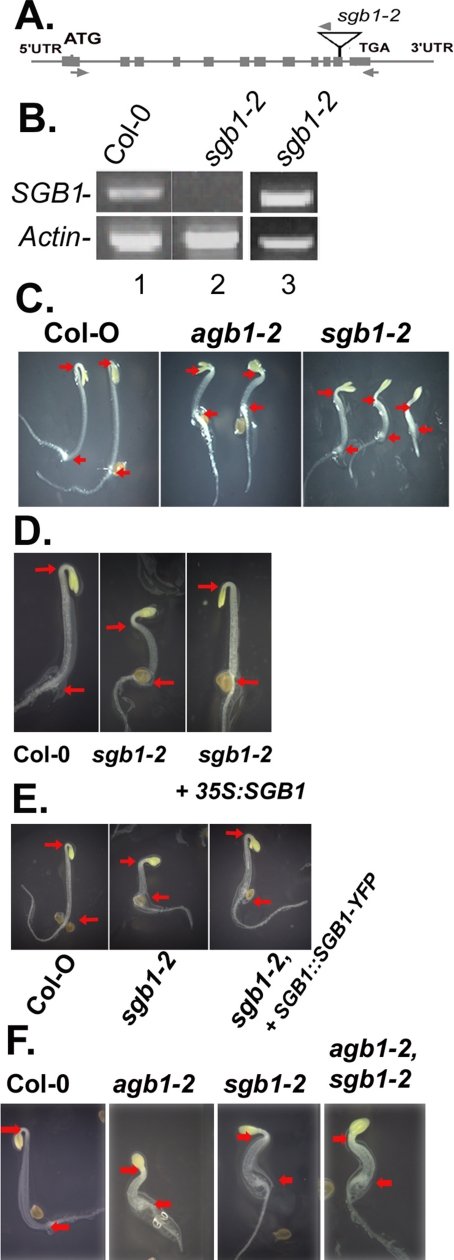
Figure 5.
SGB1 recessive mutants have overlapping phenotypes to agb1-2. (A) The sgb1-2 allele contains a T-DNA insertion in the SGB1 gene in the penultimate exon (T-DNA insert not drawn to scale). Arrows represent position of gene primers and arrowheads are T-DNA right border primers. (B) SGB1 mRNA was analyzed in young leaves by using RT-PCR as described in Materials and Methods. Lanes 1 and 2 represent RT-PCR using the 5′ and 3′ SGB1 primers (arrows). Lane 3 shows the RT-PCR product using the 5′ gene primer (left arrow) and the RB primer (arrowhead, Supplemental Table S1). Actin 2 primers in the same reactions were used for normalization (product = 0.9 kb). The SGB1 PCR product is 1.5 kb. The sgb1-2 PCR product is 1.6 kb. (C) sgb1-2 showed similar morphology to agb1-2 with shorter hypocotyls and open hooks. Red arrows mark the positions of the root–shoot transition zone (left arrow) and hook apex (right arrow), respectively, for hypocotyl length comparison. Seedlings were grown on 1/2 MS medium in dark for 2 d. (D) The sgb1-2 mutant was genetically complemented with a 35S driven SGB1 cDNA (D) or a SGB1 promoter-driven SGB1-YFP translational fusion cDNA (E). (F) The agb1-2 sgb1-2, double mutant showed similar 2 d-phenotypes as the parents with open hook and short hypocotyl; no additive or synergistic phenotypes were observed.