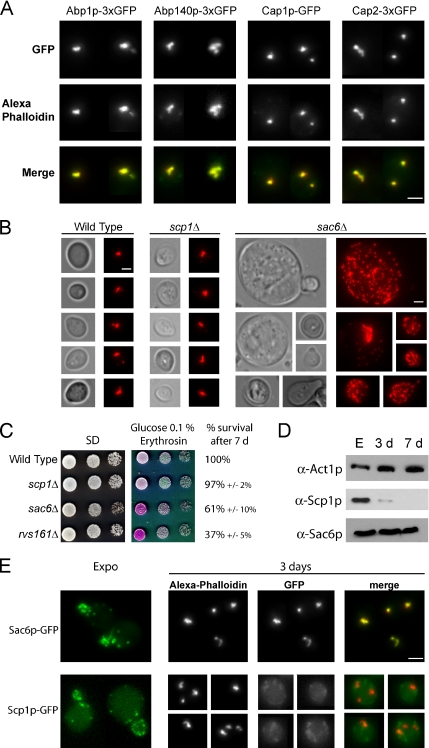
Figure 3.
(A) Colocalization of actin bodies with various actin-binding proteins. Wild-type yeast cells expressing different ABPs fused to three tandem GFP copies at a native level were grown for 2 d at 30°C in SD casa medium. Cells were fixed and stained with Alexa-phalloidin. In the merged bottom panel, GFP is shown in green, and Alexa-phalloidin–stained F-actin is shown in red. Images are 2D maximal projection of 3D image stacks. (B) Actin bodies formation in two actin-bundling protein mutants: sac6Δ and scp1Δ. Wild-type (left), scp1Δ (middle), and sac6Δ (right) cells were grown for 3 d in YPDA medium, fixed, and stained with Alexa-phalloidin. Bar, 2 μm. (C) Actin-bundling mutants survival upon starvation and in stationary phase. Serial dilutions were spotted onto regular SD casa WAU medium or synthetic medium containing casa, WUA, 0.1% glucose, and erythrosine, a dye that stains dead cells pink (Bonneu et al., 1991). Viability of the strains after 7 d of growth at 30°C in YPDA medium is indicated. Viability was assessed as described in Materials and Methods. (D) Steady-state levels of Sac6p and Scp1p at different growth phases. Samples of wild-type cells were taken in exponential phase, after 3 d (3 d) or 7 d (7 d) of culture at 30°C in YPDA medium. (E) Localization of Sac6p and Scp1p in stationary phase. Yeast cells expressing either Sac6p-GFP or Scp1p-GFP were grown in SD casa medium at 30°C. Left, GFP fluorescence is shown in living exponentially growing cells. In the following panels, cells grown for 3 d at 30°C were fixed and stained with Alexa-phalloidin. In the merged panel, GFP is shown in green, and Alexa-phalloidin–stained F-actin is shown in red. Images are 2D maximal projection of 3D image stacks. Bar, 2 μm.