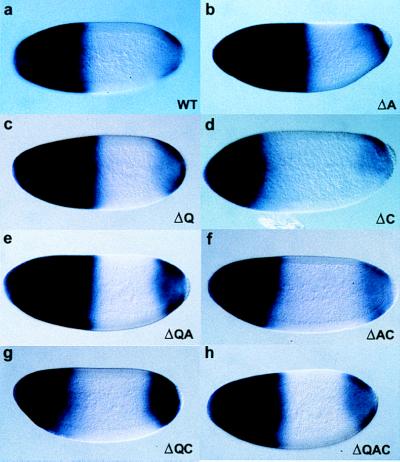
Figure 3.
hb RNA in situ hybridization of embryos from females homozygous for the strong bcdE1 allele and carrying: (a) two copies of a wild-type rescue construct; or (b–h) two copies of the Bcd deletion construct (representing the best rescuing lines), as indicated on each panel. In situ hybridization was performed with antisense probe for hb on whole-mount embryo preparations from the different transgenic lines containing Bcd deletion variants. The posterior boundary of the hb domain of expression is significantly moved anteriorly in embryos laid by females homozygous for the bcdE1 mutation and carrying two copies of the transgene: lines BcdΔC (d), BcdΔAC (f), and BcdΔQC (g). The BcdΔQ (c) and BcdΔQA (e) lines show normal amounts of hb expression within an enlarged domain. The BcdΔA line (b) exhibits a widely enlarged domain of hb transcription. The domain of expression mediated by the BcdΔQAC line that is able to rescue the bcdE1 phenotype to viability (h) appears slightly enlarged compared with wild-type Bcd.