Figure 4.
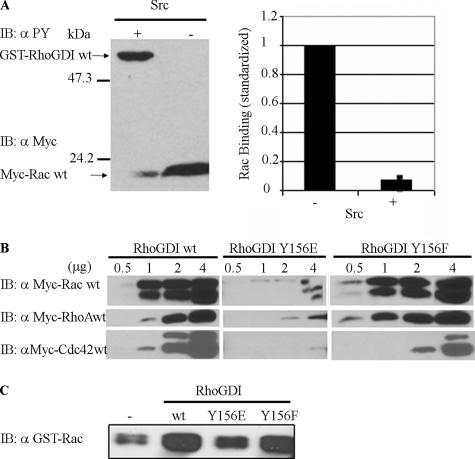
Tyrosine-phosphorylated RhoGDI and a RhoGDI phosphomimetic mutant exhibit less affinity for Rac, Rho, and Cdc42. (A) Myc-tagged Rac1 was pulled down from cell lysates by recombinant GST-RhoGDI immobilized on glutathione beads either without (−) or with (+) in vitro phosphorylation by recombinant active Src (left panel), as in Materials and Methods. Pulldowns were immunoblotted for both phospho-tyrosine with 4G10 (αPY) and the presence of associated Rac1 with myc mAb 9E10 (αMyc). The results from three experiments were quantified (right panel) and are shown as mean ± SE. (B) Myc-tagged Rac1-, RhoA-, and Cdc42-expresing cell lysates were incubated with the indicated amounts (in micrograms) of recombinant GST-RhoGDI constructs immobilized on glutathione beads and then pulled down by centrifugation, washed, and analyzed. Substitution in RhoGDI of tyrosine 156 with glutamic acid (Y156E), but not with phenylalanine (Y156F), mimics the results observed with Src-phosphorylated RhoGDI in A by reducing complex formation with all three Rho GTPases at all levels of added GDI protein. (C) The ability of the indicated pure recombinant RhoGDI constructs to extract GST-Rac1 from Sf9 cell membranes was determined, as in Materials and Methods. There was a small amount of Rac1 that became soluble even in the absence of RhoGDI (shown as − control). Results shown above are typical of at least three independent experiments.