Figure 1.
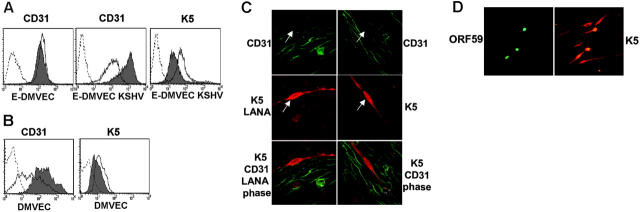
Reduced CD31 expression on KSHV infected E-DMVECs correlates with spontaneous or PMA-induced expression of K5. (A) Flow cytometry of CD31 and K5 expression in uninfected (E-DMVEC) or infected cells (E-DMVEC KSHV) treated with PMA (dark line, no shading) or untreated (gray shading) for 48 hours. Cell-surface–expressed CD31 was detected on intact cells using monoclonal antibody JC/704; the dotted line indicates fluorescently labeled secondary antibody only. To reveal K5 expression, KSHV-infected cells or uninfected E-DMVECs (dotted line) were permeabilized and stained with K5-specific antibody 328C7 as well as fluorescently labeled secondary antibody. (B) Flow cytometry of CD31 or K5 expression of uninfected primary DMVECs ( ) or primary DMVECs 48 hours after infection with KSHV (dark line, no shading). (C) Spontaneous K5 expression in latently infected E-DMVECs in the absence of PMA. Left column shows KSHV-infected E-DMVECs stained for CD31 (green), K5 (red), and LANA-1 (red). LANA-1 staining is evident by a typical punctate nuclear pattern. Right column shows staining as in the left column, but without antibodies to LANA-1. The arrow indicates a K5-expressing cell. Note the lack of CD31 expression on K5-expressing cells, whereas LANA-expressing, but K5-negative, cells still express CD31. (D) Simultaneous evaluation of K5 and ORF59 in KSHV-infected DMVECs after PMA induction (48 hours). Monolayers were stained for expression of K5 and ORF59 using specific antibodies and isotype-specific secondary antibodies (Alexa 488 IgG1 for ORF59 and Alexa 594 IgG2b for K5). All cells expressing the IE protein K5 expressed the E protein Orf59, but 4 to 5 times as many cells expressed K5 only. Similar ratios, but lower absolute numbers, were observed in the absence of PMA (not shown).
) or primary DMVECs 48 hours after infection with KSHV (dark line, no shading). (C) Spontaneous K5 expression in latently infected E-DMVECs in the absence of PMA. Left column shows KSHV-infected E-DMVECs stained for CD31 (green), K5 (red), and LANA-1 (red). LANA-1 staining is evident by a typical punctate nuclear pattern. Right column shows staining as in the left column, but without antibodies to LANA-1. The arrow indicates a K5-expressing cell. Note the lack of CD31 expression on K5-expressing cells, whereas LANA-expressing, but K5-negative, cells still express CD31. (D) Simultaneous evaluation of K5 and ORF59 in KSHV-infected DMVECs after PMA induction (48 hours). Monolayers were stained for expression of K5 and ORF59 using specific antibodies and isotype-specific secondary antibodies (Alexa 488 IgG1 for ORF59 and Alexa 594 IgG2b for K5). All cells expressing the IE protein K5 expressed the E protein Orf59, but 4 to 5 times as many cells expressed K5 only. Similar ratios, but lower absolute numbers, were observed in the absence of PMA (not shown).