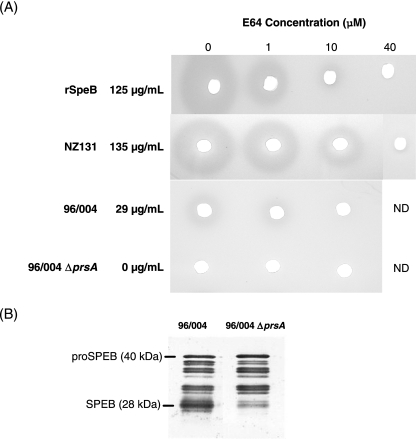
FIG. 5.
Disruption of prsA abolishes functional SpeB activity but not protein production. A milk protein hydrolysis plate assay (A) and a SpeB-specific Western blot (B) were used to demonstrate SpeB enzymatic activity and to detect SpeB protein production, respectively. (A) Culture supernatant fluids from the wild-type parent strain 96/004 or its prsA isogenic deletion mutant were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of the irreversible cysteine protease inhibitor E64, and then 20 μl was plated into wells in milk agar plates as described in Materials and Methods. Supernatant from the high-level-SpeB-producing strain, NZ131, and recombinant SpeB with or without E64 served as positive controls. After 18 h, zones of casein hydrolysis were observed. The amount of SpeB (μg/ml) in each preparation in the absence of E64 is shown and was determined by casein hydrolysis assay. ND, not done. (B) Western blotting of supernatants from the wild-type parent GAS 96/004 or its prsA deletion mutant was performed using anti-SpeB-specific antibody.