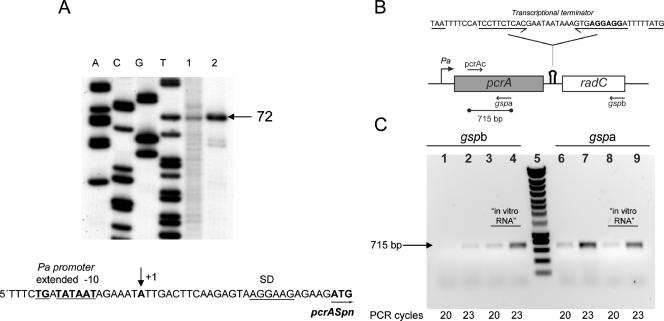
FIG. 2.
Transcriptional analysis of the pcrA-radC operon in S. pneumoniae. (A) Primer extension analysis for determination of the transcription start site of pcrA,. RNA samples from S. pneumoniae (lane 1) and E. coli harboring plasmid pCR2.1PN (lane 2) were reverse transcribed using 32P-labeled primer pcrAext (see Materials and Methods). A single extended 72-nt DNA was observed, which located the transcription start site at the A residue (+1) indicated by an arrow in the DNA sequence. Lanes A, C, G, and T contained DNA sequencing reaction products obtained using the same primer. The extended −10 sequence of the Pa promoter (underlined boldface type), the ribosome-binding site (SD) (underlined), and the first codon of pcrA (boldface type underlined with an arrow) are also indicated. (B) Schematic diagram of the genetic structure of the pcrA-radC locus, showing the positions of the Pa promoter and of the putative rho-independent transcriptional terminator (hairpin symbol). The DNA sequence encompassing the putative intrinsic terminator is shown above the schematic diagram, and the convergent arrows indicate the inverted repeat located upstream of the T tract. The pcrA stop codon and the radC start codon are underlined, and the putative radC Shine-Dalgarno sequence is indicated by boldface type. The primers used for RT (gspa and gspb) or PCR (pcrAc and gspa) are indicated by arrows. The location of the 715-bp PCR-amplified fragment is also shown. (C) RT-PCR analysis. Two cDNAs spanning pcrA-radC or pcrA were synthesized using total RNA prepared from S. pneumoniae R6 and oligonucleotide gspb or gspa, respectively. Amplified dsDNA was then obtained by PCR using oligonucleotides pcrAc and gspa as primers. Aliquots from the PCR mixtures were taken after 20 and 23 amplification cycles. Lanes 1 to 4, PCR products from pcrA-radC cDNA; lanes 6 to 9, PCR products from pcrA cDNA; lanes 3, 4, 8, and 9, control RT-PCRs using pcrA-radC “in vitro RNA” as the template; lane 5, DNA molecular weight standard (Smartladder; Eurogentec).