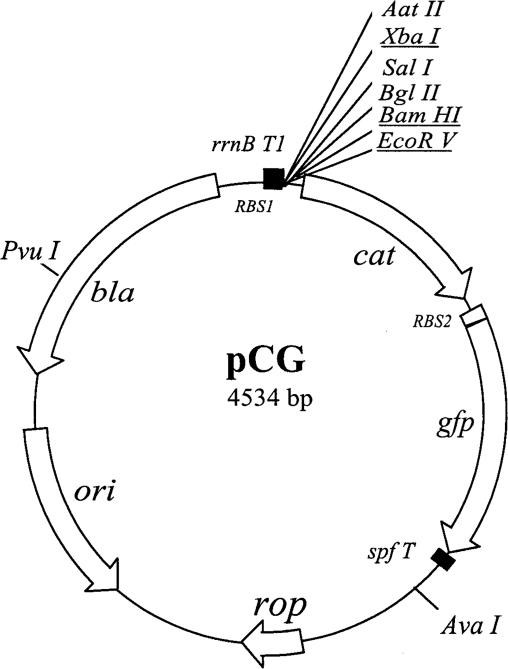
FIG. 1.
pCG vector for assaying in vivo promoter activity. pCG is a derivative of pRV1 (50). The PvuI/AvaI fragment, which contains rrnB T1 multiple cloning sites (MCS), chlamydial tuf ribosomal binding site 1 (RBS1), and the reporter cat gene from pRV1, was ligated with the PuvI/AvaI fragment of pBR322, which contains the ColE1 replication origin and rop, resulting in pRVB. pRVB was then modified by (i) replacement of the MCS; (ii) insertion of an enhanced E. coli RBS (RBS2), an improved gfp gene, encoding GFP (36), and the second reporter gene directly downstream of the cat gene; and (iii) addition of a synthetic spf terminator (spfT) downstream of the gfp gene, creating pCG. Thus, pCG contains the MCS convenient for cloning test promoters, promoterless cat-gfp, the ColE1 replicon, a bla gene allowing ampicillin selection, the transcriptional terminator rrnB T1, preventing readthrough into the cat-gfp operon, and spfT, preventing interference from opposing transcription. The sites used for cloning test promoters in this study are underlined.