FIG.9.
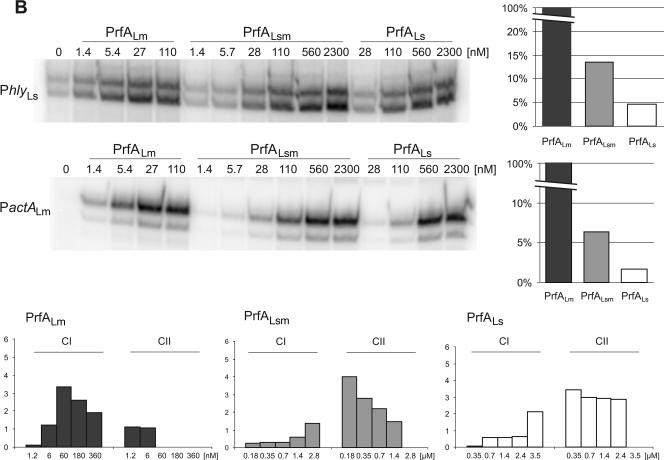
Replacement of the C-terminal 38 amino acids of PrfALs with those of PrfALm. (A) ClustalW alignment of the PrfA proteins of L. monocytogenes (PrfALm), L. ivanovii (PrfALi), and L. seeligeri (PrfALs). Identical amino acids are shaded in black, and similar amino acids are shaded in gray. Amino acid substitutions leading to a constitutively active PrfA are marked. (B) In vitro transcription assay with increasing concentrations of PrfALm, the hybrid PrfALsm, and PrfALs using 16 nM promoter template DNA and 1.9 nM RNA polymerase. The mRNA was marked with [α-32P]CTP during transcription. The transcription-activating potentials of the different PrfA proteins compared to that of PrfALm are given in the graphs to the right. The graphs in the lower part of the panel below show the amounts of CI and CII measured in EMSAs. The components were 5 nM 32P-marked promoter DNA (PhlyLm) and 1.5 nM RNA polymerase, and the PrfA concentration is given in the figure. Quantification of CI and CII complexes was performed using ImageMaster (Amersham). The data shown here represent the results of one of three independently performed experiments.