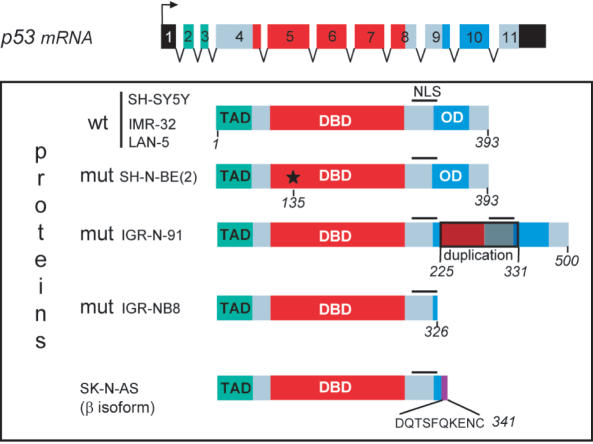
Figure 9.
Structure of p53 proteins in different neuroblastoma cell lines. The three functional domains are represented: TAD, transactivation domain; DBD, DNA-binding domain; OD, oligomerization domain. The wild-type p53 gene in SH-SY5Y, IMR-32 and LAN-5 cells contains 11 exons that encode 393 amino acids. In SK-N-BE(2) cells, p53 is mutated at codon 135 (*), which converts cysteine to phenylalanine. In IGR-N-91 cells, a duplication of exons 7-8-9 adds an additional 107 amino acids leading to a total of 500. In SK-N-AS cells, a mutation due to alternate splicing downstream of exon 9 leads to a protein of 341 amino acids whereas in IGR-NB8 cells, the p53 protein ends at 326 amino acids owing to the mutation E326STOP.