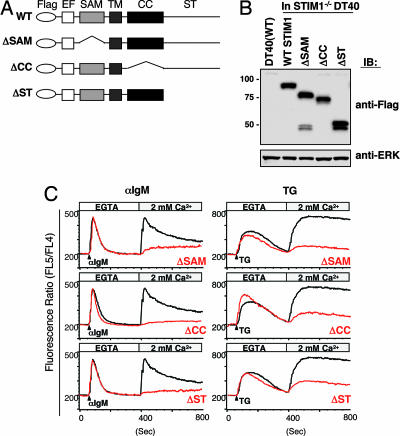
Fig. 2.
STIM1 utilizes its multiple functional domains for Ca2+ influx. (A) Schematic representation of STIM1 mutants and the functional domains, including Flag-tagged, SAM, coiled-coil (CC), and Ser/Thr-rich C-terminal (ST) domains. Flag-tagged STIM1 cDNAs encoding deletion mutations were transfected into STIM1-deficient DT40 B cells. EF, EF-hand motif; TM, a single transmembrane. (B) Expression of Flag-STIM1 in various mutant DT40 cells. Whole-cell lysates were fractionated by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-Flag mAb (Upper) or anti-ERK Ab (Lower). (C) STIM1 utilizes the multiple functional domains for Ca2+ influx. Intracellular Ca2+ release and influx in response to BCR with anti-IgM mAb (Left) and TG stimulation (Right) in STIM1-deficient DT40 cells expressing WT Flag-STIM1 (black lines) or mutants (red lines) were measured by Ca2+ add-back methods.