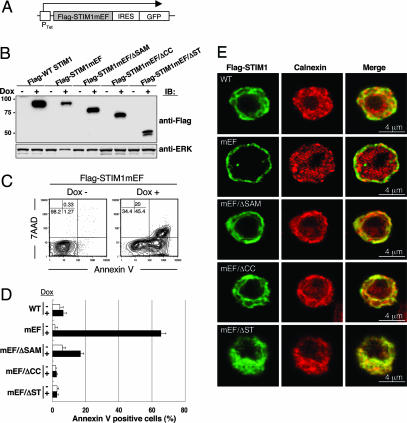
Fig. 5.
Expression of STIM1 EF-hand mutants, but not double mutants of EF hand and its functional domains, induces cell death. (A) Schematic representation of the doxycycline-inducible construct of STIM1 EF-hand mutants. cDNA of Flag-tagged STIM1 EF-hand mutants (mEF; D76A/D78A/N80A/E87A) and double mutation of mEF in addition with ΔSAM (mEF/ΔSAM), ΔCC (mEF/ΔCC), and ΔST (mEF/ΔST) linked by an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) to a cDNA encoding EGFP were transfected into STIM1-deficient DT40 B cells. Ptet, doxycycline responsible promoter. (B) Expression of STIM1 mEF mutants in DT40 cells after doxycycline induction for 24 h was detected by immunoblotting with anti-Flag mAb (Upper). ERK protein was detected as a loading control (Lower). (C) The expression of STIM1 EF-hand mutants induced cell death. STIM1-deficient DT40 cells expressing Flag-STIM1mEF were stained with phycoerythrin-annexin V and 7-amino-actinomycin D before and after 24 h doxycycline (Dox) induction and were analyzed by flow cytometry. The induction of STIM1 mutants was monitored by GFP (data not shown), and doxycycline-induced cell death was detected in the GFP-positive gate. (D) Cells were stained with phycoerythrin-annexin V before and after doxycycline induction for 24 h and were analyzed by flow cytometry. Bar graphs show the percentage of annexin V-positive cells among total (Dox−) and GFP+ (Dox+) cells. These results are representative of three independent experiments (means ± SE). (E) Localization of various STIM1 EF-hand mutants. Various Flag-STIM1 (green) and calnexin (red) immunofluorescence staining was shown after 24 h of doxycycline induction.