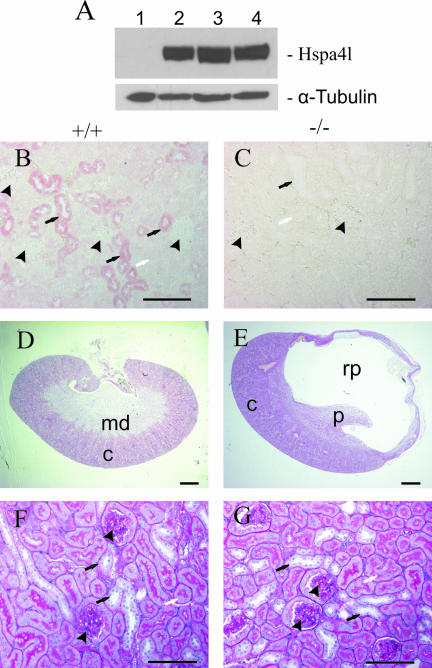
FIG. 6.
Expression of Hspa4l in kidneys and histological analysis of hydronephrosis in Hspa4l-deficient mice. (A) Immunoblot with proteins extracted from kidneys of a Hspa4l-null mouse (lane 1), an untreated mouse (lane 2), a water-deprived mouse (lane 3), and a mouse treated with 3% NaCl in the drinking water (lane 4). The blot was incubated with anti-Hspa4l and -α-tubulin antibodies. (B and C) Immunohistological staining of renal sections from wild-type and Hspa4l-null mice with anti-Hspa4l antibody. Views at the level of the cortex show the localization of Hspa4l in the cytoplasm of epithelial cells of distal tubules (B). In contrast, there was no immunostaining in kidneys of null mice (C). (D and E) Whole kidney images of renal sections from wild-type (D) and Hspa4l-deficient (E) mice at 5 months old. The renal pelvis was grossly dilated in mutant mice. Detailed images of sections from a wild-type kidney (F) and a hydronephrotic kidney (G) at the level of the cortex do not show detectable structural changes in glomeruli (arrowheads) or proximal (white arrows) and distal (black arrows) tubules. c, cortex; md, medulla; p, papilla; rp, renal pelvis. Bars: panels D and E, 1 mm; panels B, C, F, and G, 200 μm.