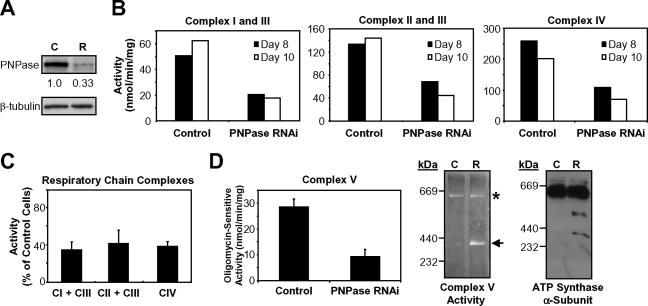
FIG. 8.
PNPase reduction impairs respiratory chain function. (A) Representative immunoblot of PNPase knockdown (R) and control (C) cells used for the experiments described below. PNPase was reduced to 33% of control HEK293 cells on day 8 after RNAi transfection by densitometry. (B) Respiratory chain complex activities in mitochondria from control and HEK293 PNPase knockdown cells measured spectrophotometrically. Activities are expressed as nmol cytochrome c reduction or oxidation/min/mg of mitochondrial protein. Data are from day 8 and day 10 of two independent PNPase knockdown experiments. (C) Summary of the data in panel B. Complex (CI, CII, CIII, and CIV) activities are expressed as percentages of the activity of control cells (normalized to 100%). (D) Reduced activity and partial dissociation of the ATP synthase in PNPase knockdown cells. Oligomycin-sensitive ATP hydrolysis activity was determined spectrophotometrically (left panel). Mitochondria from control and PNPase knockdown cells were analyzed by BN-PAGE followed by in-gel ATP hydrolysis activity staining (middle panel) or immunoblotting for the α-subunit of the F1-ATP synthase subcomplex (right panel). Symbols: *, fully assembled FoF1-ATP synthase complex (theoretical molecular mass, ∼600 kDa); ←, F1 subcomplex (theoretical molecular mass, 371 kDa).