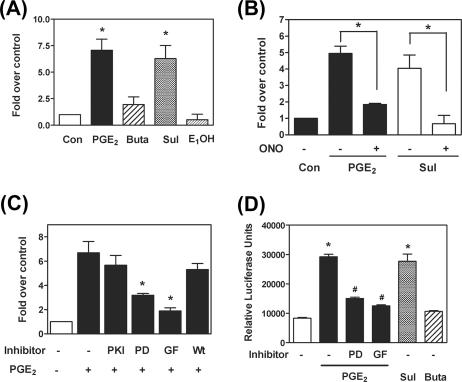
FIG. 3.
PGE2-induced FGF-9 expression is mediated via the EP3 receptor-dependent signaling pathway. (A) Serum-starved stromal cells were treated with 1 μM PGE2, 10 μM butaprost (Buta), 10 μM sulprostone (Sul), or 10 μM PGE1-OH (E1OH) for 12 h. Data show means ± SEM for six independent experiments using different batches of cells. Asterisks denote significant differences from data for the control group (P < 0.05). (B) Serum-starved stroma cells were treated with 1 μM PGE2, 10 μM sulprostone in the presence or absence of ONO-AE3-240 (selective EP3 antagonist) for 12 h (n = 4). Asterisks indicate significant differences from data for the PGE2- or sulprostone-treated group (P < 0.05). (C) Serum-starved stromal cells were preincubated for 30 min with 25 μM PKI, 10 μM PD98059 (PD), 5 μM GF109203 (GF), or 1 μM wortmannin (Wt) and then treated with 1 μM PGE2 for 12 h (n = 6). Asterisks indicate significant differences from data for the PGE2-treated group (P < 0.05). (D) Ectopic endometriotic stromal cells were transfected with the FGF-9 promoter construct (nucleotides −1949 to +217) and treated with 1 μM PGE2 for 12 h in the presence or absence of different selective inhibitors, and then luciferase activity was analyzed. The promoter activities (relative light units [RLU]) were calculated by dividing firefly signal levels by Renilla signal levels (n = 6). Asterisks indicate significant differences from data for the control group, while # indicates significance compared to data for the PGE2-treated group (P < 0.05).