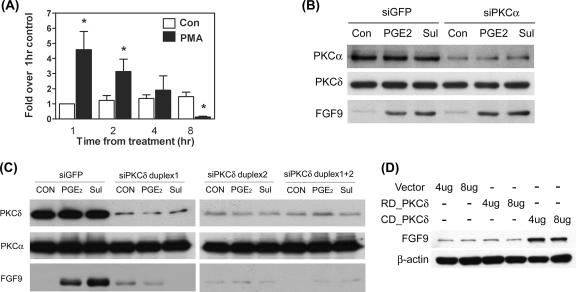
FIG. 4.
PKCδ is critical for PGE2-induced FGF-9 expression. (A) Serum-starved cells were treated with 30 nM PMA or vehicle for the indicated times, and expression levels of FGF-9 mRNA were determined by QC-RT-PCR. Data show means ± SEM for six independent experiments using different batches of cells. Asterisks indicate significant differences from data for the control group at each time point. (B) A representative picture shows the expression of FGF-9 protein after transient transfection with siPKCα. Stromal cells were transiently transfected with siPKCα siRNA or control siRNA as described in Materials and Methods. After transfection, serum-starved cells were treated with or without 1 μM PGE2 or 10 μM sulprostone (Sul) for 12 h. Equal amounts of total cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against PKCα (upper panel), PKCδ (middle panel), and FGF-9 (lower panel). (C) A representative picture shows the expression of FGF-9 protein after transient transfection with siPKCδ. Stromal cells were transiently transfected with siPKCδ duplex 1, siPKCδ duplex 2, siPKCδ duplex 1 plus duplex 2, or control siRNA (siGFP) as described in Materials and Methods. After transfection, serum-starved cells were treated with or without 1 μM PGE2 or 10 μM sulprostone for 12 h. Equal amounts of total cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against PKCα (upper panel), PKCδ (middle panel), and FGF-9 (lower panel). (D) Stromal cells were transiently transfected with 4 μg or 8 μg of control vector pEGFP-N2 only (vector), the catalytic subunit of PKCδ (CD_PKCδ), or the regulatory subunit of PKCδ (RD_PKCδ) for 12 h. Equal amounts of cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-FGF-9 or anti-β-actin antibodies, sequentially. These experiments were repeated four times using different batches of cells, and the results were similar.