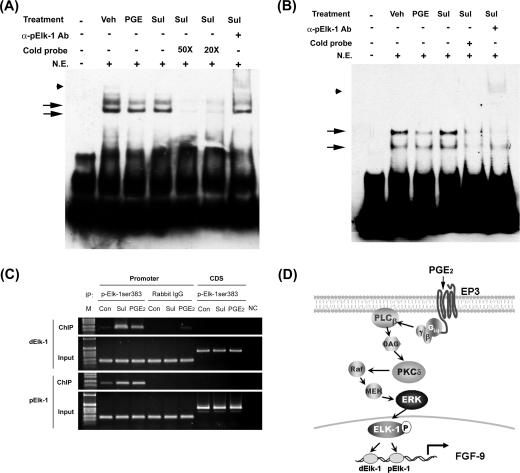
FIG. 7.
Binding of Elk-1 to the fgf-9 promoter is enhanced after PGE2 treatment. (A and B) Representative EMSA pictures show in vitro binding of Elk-1 to the two predicted Elk-1 elements in the fgf-9 promoter. Nuclear extract of vehicle, PGE2, or sulprostone-treated stromal cells was incubated with biotin-labeled probe containing the dElk-1 (A) or pElk-1 (B) element of the fgf-9 gene promoter in the presence or absence of excess cold probe. Arrows indicate the DNA/protein complex. Anti-phospho-Elk-1 antibody was added to detect the supershift of the protein/DNA complex (arrowhead). Sul, sulprostone. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay demonstrates in vivo binding of Elk-1 to the predicted dElk-1 and pElk-1 sites. Immunoprecipitated DNA using anti-phospho-Elk-1 antibody, control rabbit immunoglobulin G (ChIP), or genomic DNA (input) was subjected to PCR amplification using primers specific for dElk-1, pElk-1 (promoter), or the downstream coding region (CDS). (D) A schematic drawing shows the signal transduction pathway mediating PGE2-induced fgf-9 gene transcription. See the text for details.