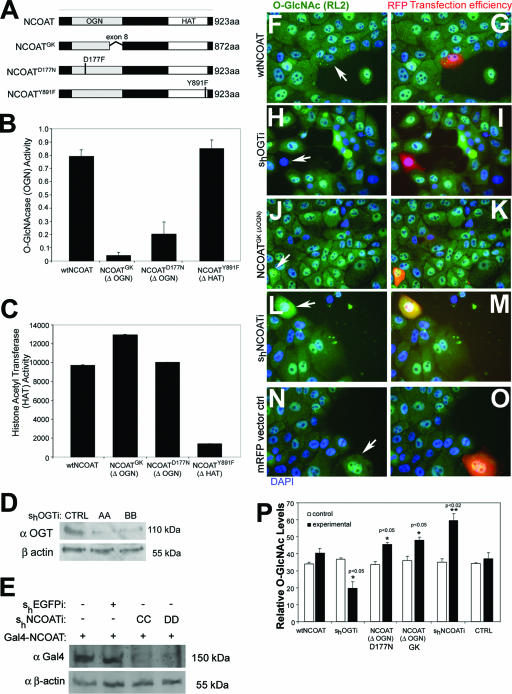
FIG. 1.
Overexpression of mutant NCOAT increases intracellular O-GlcNAc levels. (A) Cartoon depiction of wild-type NCOAT, NCOATGK splice variant, NCOATD177N, and NCOATY891F. (B) O-GlcNAcase activity for the indicated NCOAT constructs was measured using an in vitro pNP-GlcNAc assay. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. (C) Results of an in vitro HAT assay for the indicated NCOAT constructs using [3H]acetyl coenzyme A to modify immobilized histone tails. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. (D) Western blot showing levels of endogenous OGT in MCF10AT whole-cell lysates in the absence or presence of short hairpin RNAi constructs (AA and BB) against OGT. (E) Western blot of Gal4(DBD) in cells transfected with cytomegalovirus-Gal4(DBD)-tagged NCOAT to test short hairpin RNAi constructs (CC and DD) against NCOAT. (F to O) Immunohistochemical detection of O-GlcNAc levels (green channel) in response to 18 h of transfection with the indicated constructs. Positive transfectants were tracked with mRFP, and DAPI (blue) was used for nuclear staining. For overexpression of NCOAT variants lacking OGN activity (ΔOGN), only the NCOATGK image is shown (J and K). (P) O-GlcNAc levels were quantified by densitometry of three separate transfectants with the indicated constructs, and arbitrary densitometric values ± standard deviations are shown. The surrounding cells were used to establish control levels for O-GlcNAc. Student's t test was used to establish significant differences, which are indicated as P values of <0.05 (*) and <0.02 (**). wt, wild type.