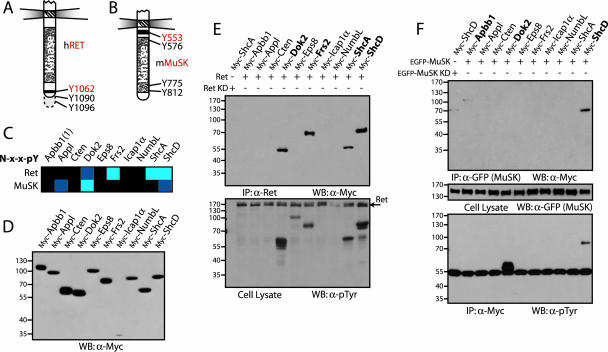
FIG. 5.
Peptide arrays identify interactions between full-length receptors and PTB domain-containing adaptor proteins. (A and B) Representation of the intracellular regions from Ret and MuSK. Common numbering of tyrosines from the Ret receptor is from Homo sapiens and from Mus musculus for MuSK. Tyrosine residues contained in NXXY motifs present on the arrays are shown in red. (C) Interaction data for PTB domains with tyrosine-phosphorylated NXXY motifs from the Ret and MuSK receptors. Domains from Dok2, Frs2, ShcA, and ShcD bound the Ret peptide. Interactions between the MuSK motif and the PTB domains of Appl, Dok2, and ShcD represented novel and potentially interesting associations. (D) Full-length PTB domain adaptor proteins were used to assess the interactions. Proteins were cloned and expressed in HEK 293T cells with N-terminal Myc tags. Production was monitored by Western blotting, using antibodies against Myc. (E) PTB domain-containing proteins were coexpressed with activated Ret. Immunoprecipitation using antibodies against the receptor, and immunoblotting with anti-Myc, revealed associated proteins (upper panel). Only those adaptors containing PTB domains able to recognize the NXXY motif of the Ret receptor in vitro were coprecipitated (shown in bold). To determine if these proteins were also phosphorylated by Ret, a Western blot using antibodies against pTyr was performed (lower panel). As a control, ShcA was also coexpressed with a kinase-dead Ret (lane 1). (F) Adaptor protein precipitation or phosphorylation by MuSK. The Myc-tagged PTB proteins were coexpressed with recombinant, EGFP-tagged MuSK in HEK 293T cells. Immunoprecipitating the receptor with anti-GFP antibodies and a Western blot using anti-Myc revealed associated proteins (upper panel). Both Apbb1 and ShcD were precipitated (in bold). Immunoblotting anti-Myc precipitations using antibodies against pTyr determined whether potential interaction partners were phosphorylated (lower panel). Dok2 and ShcD were highly phosphorylated by MuSK (in bold). The middle panel shows a Western blot on cell lysates using anti-GFP antibodies to confirm expression of the receptor. As a control, ShcD was also coexpressed with a kinase-dead MuSK (lane 1). WB, Western blotting; IP, immunoprecipitation; KD, kinase dead.