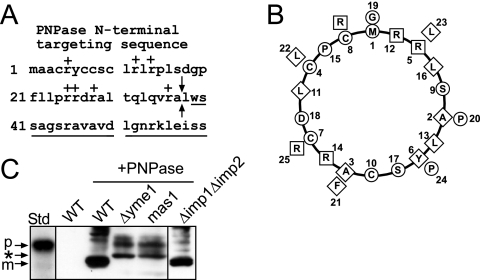
FIG. 1.
PNPase processing is inhibited in yeast lacking the MPP and i-AAA protease Yme1. (A) Schematic showing the N-terminal targeting sequence within the N terminus of PNPase. The basic residues are indicated with a “+,” the sequence of the mature PNPase is underlined, and the arrows mark the MPP cleavage site. (B) The first 26 amino acids were placed on a helical wheel (40). The boxes mark basic residues, the diamonds mark hydrophobic residues, and the circles mark the remaining residues. (C) PNPase was expressed heterologously in yeast under control of the Cu2+-inducible CUP1 promoter. Expression was analyzed in a total lysate by immunoblotting with polyclonal anti-PNPase antibody. PNPase was expressed (+PNPase) in strains defective in MPP (mas1), IMP (Δimp1Δimp2), and Yme1 (Δyme1) and in the WT strain. The precursor form (p) is marked for the in vitro-translated standard (Std), and the mature form (m) is marked for PNPase expressed in WT yeast (WT +PNPase). The asterisk marks products that accumulate when PNPase import and assembly are impaired.