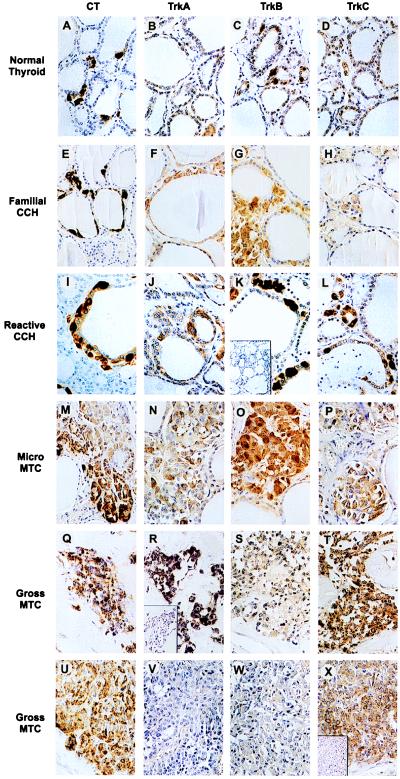
Figure 1.
Immunohistochemical staining of Trk family of receptors in normal thyroid C cell hyperplasia. (A–D) A representative normal thyroid with the C cells strongly staining for calcitonin (A) and trkB (C) with no trkA (B) or trkC (D) immunoreactivities. (E–H) C cell hyperplasia (CCH) from a patient with MEN 2A, stained for calcitonin (E), trkA (F), trkB (G), and trkC (H). (I–L) A thyroid containing a reactive C cell hyperplasia secondary to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Strong staining of the C cells can be seen with the calcitonin (I), trkB (K), and trkC (L) antibodies and moderate staining with the trkA (J) antibody. The inset in K is a representative example of the loss of staining observed when the trkB antibody is preincubated with its immunizing peptide. (M–P) Microscopic MTC contained within the thyroid of a patient with MEN2A, stained for calcitonin (M), trkA (N), trkB (O), and trkC (P). The trkA and trkC antibodies moderately stained both the C cell hyperplasia and microscopic MTC, while the trkB antibody strongly stained both areas. Q–T and U–X are two different gross MTC tumors stained for calcitonin (Q and U), trkA (R and V), trkB (S and W), and trkC (T and X). One tumor was strongly positive for trkA (R) and moderately positive for trkB (S) while the other exhibited no trkA staining (V) and only weak trkB staining (W). Both tumors were strongly positive for trkC (T and X). The insets in R and X are representative examples of the loss of trkA or trkC staining observed when the respective antibody was preincubated with its appropriate immunizing peptide.