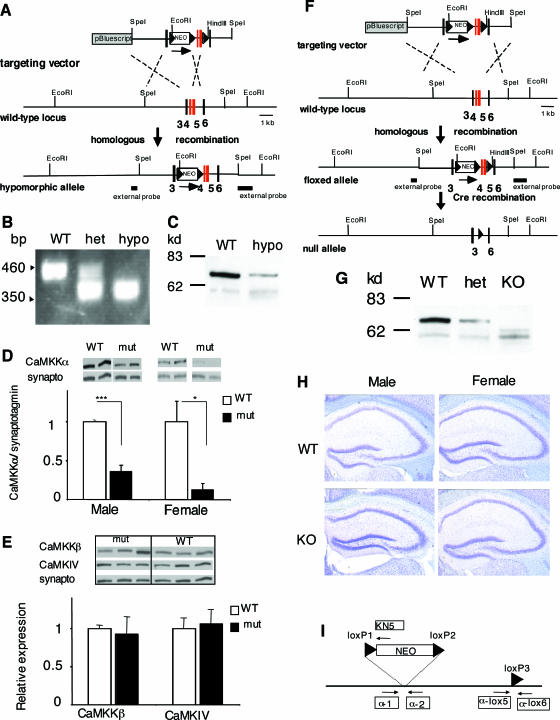
FIG. 1.
Generation of Camkk1 hypomorphic and Camkk1 null mutant mice. (A) Gene targeting to obtain Camkk1 hypomorphic mutants. The targeting vector had exons 4 and 5 of the mouse Camkk1 gene flanked by a single loxP site and a “floxed” NEO gene. The loxP sites are shown as triangles. The single loxP site was lost during homologous recombination. Exon numbers are shown in bold type below the diagrams. (B) Genotyping of Camkk1 hypomorphic mutants was performed by PCR. DNA from wild-type (WT), heterozygous (het), and homozygous (hypo) mutant mice was used. (C) Representative immunoblot of CaMKKα expression in hippocampus of male WT and male hypomorphic mutants. (D) Quantification of the signals from immunoblots showed a decreased CaMKKα expression in male and female hypomorphic mutants (six mice in both the male WT group and male mutant [mut] group; three mice in the female WT group and four mice in the female mutant group). Values are means plus standard errors of the means (error bars). Values that are significantly different are indicated by asterisks (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001). synapto, synaptotagmin. (E) Immunoblot analysis showed normal hippocampal expression of CaMKKβ and CaMKIV in male hypomorphic mutants (three mice in the WT group and three mice in the mutant group). (F) Gene targeting for obtaining Camkk1 null mutants. “Floxed” exons 4 and 5 were removed by Cre recombination. (G) The null mutants (knockout [KO]) did not express CaMKKα protein in the hippocampus. (H) Coronal brain sections of Camkk1 null mutant and WT mice stained with cresyl violet showed no alterations in neuroanatomy in the hippocampus at the light microscopic level (×4 magnification). (I) Primers for genotyping of mutants. The primers used to genotype hypomorphic mutants were α-1, α-2, and KN5, and the primers used to identify null mutants were α-1, α-lox5, and α-lox6.