FIG. 5.
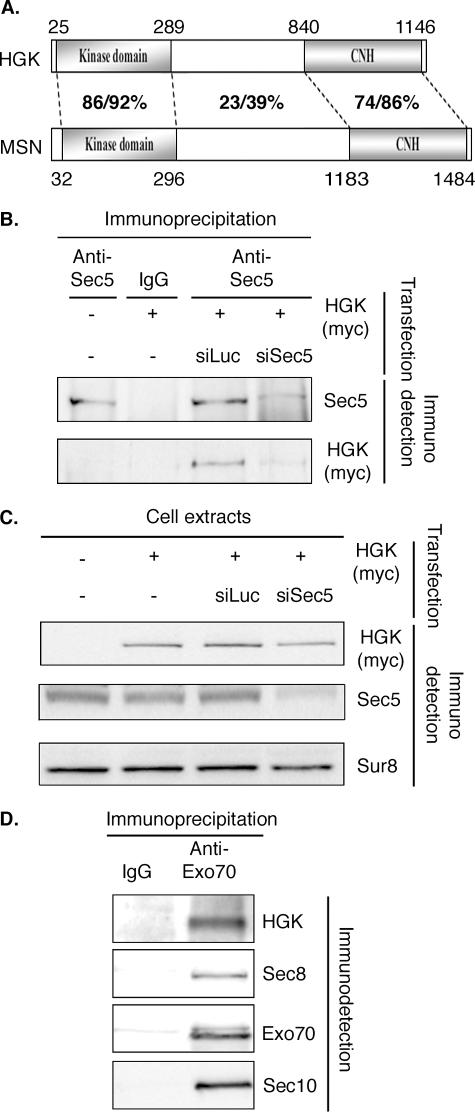
The exocyst complex interacts with HGK/MAP4K4, an activator of the JNK pathway. (A) Schematic representation of human and Drosophila MAP4K4 HGK and MSN. Domains are indicated as well as the percent identity/similarity between the different regions of the human and fly proteins. The global identity and similarity for the whole proteins are 43 and 53%, respectively. For the sake of simplicity, we show only isoform 1 of HGK (NP_004825). The difference between the three reported isoforms affects the regions flanking the kinase domain and the CNH domain. (B) Sec5 interacts with HGK. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and the indicated siRNAs. Whole-cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibodies. Myc-HGK was present in immunoprecipitates obtained with anti-Sec5 antibodies (58) in cells transfected with a plasmid expressing myc-HGK. This result was specific: when Sec5 protein was depleted by specific siRNA, less Sec5 and less myc-HGK were detected in the anti-Sec5 immunoprecipitate, showing that myc-HGK was not precipitated directly by the anti-Sec5 antibodies. (C) siRNAs against Sec5 are specific. The cells extracts used in panel B for immunoprecipitation were probed for the presence of the indicated proteins. The siRNA against Sec5 (siSec5) reduced strongly the amount of Sec5, while myc-HGK looks only marginally affected. (D) HGK is immunoprecipitated with the Exo70 subunit of the exocyst complex. NRK cells transfected with a plasmid expressing myc-HGK were lysed, and cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were tested for the presence of other subunits of the exocyst and of HGK. HGK was detected in the immunoprecipitate with anti-Exo70. IgG, immunoglobulin G; siLuc, siRNA against luciferase.