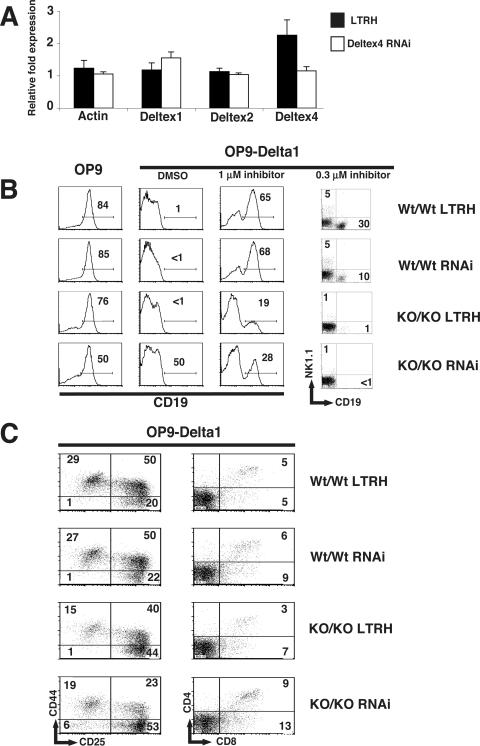
FIG. 6.
Notch signals are more potent in stem cells expressing low levels of Deltex1, Deltex2, and Deltex4. (A) Inhibition of Deltex4 mRNA in stem cells from fetal liver. Fetal liver cells from day 14 embryos were transduced with retroviral supernatants expressing empty vector (LTRH) or a pool of two Deltex4 siRNAs, and RNA was isolated after 4 days of culture. Expression of Deltex1, Deltex2, Deltex4, and β-actin was determined by TaqMan RT-PCR analysis. Relative cDNA expression for cDNAs was normalized to the value for HPRT. (B) Expression of CD19 on fetal liver stem cells derived from wild-type (Wt/Wt) or Deltex1/Deltex2 double-knockout (KO/KO) embryos infected with empty vector (LTRH) or the Deltex4 RNAis used for panel A (RNAi). Day 14 embryos were typed for Deltex1 and Deltex2 by PCR on genomic DNA, infected with the indicated retroviruses, and cultured in the presence of SCF and IL-7 for 2 days. Lineage-negative, human CD4+ stem cells were sorted and plated at 2,000 cells per well on OP9 or OP9-Delta1 in the presence of carrier (dimethyl sulfoxide) or increasing doses of a γ-secretase inhibitor. Expression of cell surface markers was assessed by FACS analysis on day 6 (histograms) or day 14 (dot plots). (C) Expression of T-lineage markers on fetal liver stem cells cultured on OP9-Delta1. DN subsets were analyzed by expression of CD44 and CD25 on day 6. CD4 and CD8 expression was examined on day 14. Numbers in quadrants indicate the frequency of cells in the quadrant shown. Data are representative of two independent experiments.