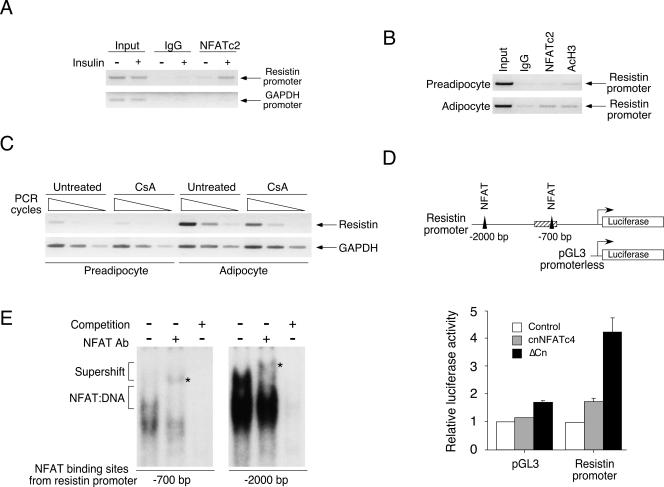
FIG. 12.
NFAT regulates resistin adipokine gene expression. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were performed to determine binding of NFAT to resistin transcription loci in the epididymal fat depot upon insulin challenge (A; see hatched box in panel D for region investigated). Recruitment of NFAT to the resistin transcription loci upon adipocyte differentiation was also shown (B). Isotype-matching IgG and/or amplification of the GAPDH loci were used as controls. Regulation of resistin gene transcription by NFAT upon adipocyte differentiation was also assessed by RT-PCR analysis (C). Effect of NFAT activation, using constitutive nuclear NFATc4 (cnNFATc4; shaded bars) or constitutive active calcineurin (ΔCn; filled bars), on the resistin promoter (−1 to −2000) and promoterless pGL3 plasmid was determined (D). Luciferase activity was normalized to β-galactosidase activity and presented. Resistin loci investigated by chromatin immunoprecipitation were illustrated as a hatched box, and filled triangles represent NFAT binding elements on the resistin promoter (D). Formation of NFAT-DNA complex at the −700-bp and −2,000-bp NFAT binding elements of the resistin promoter was assessed by gel mobility shift assays (E). Specificity of the NFAT:DNA complex was assessed by supershift analysis using antibody against NFAT (see asterisk for supershifted complex) and competition using excess amounts of unlabeled NFAT oligonucleotides.