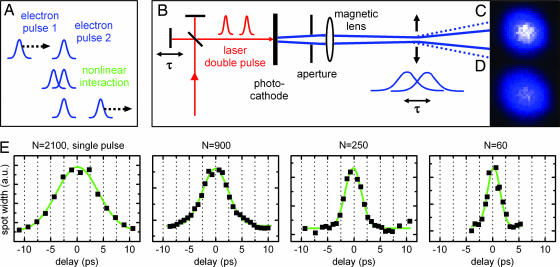
Fig. 5.
Electron pulse autocorrelation. (A) Concept of an autocorrelation measurement with electron pulses exploiting the nonlinearity in free space. (B) Experimental arrangement. A laser double-pulse generates two identical electron pulses with a delay. A magnetic lens system focuses the electron pulses toward a narrow spatial waist, where Coulomb repulsion leads to a spatial beam broadening that depends on delay time. (C and D) Beam profiles are shown without (C) and with (D) temporal overlap between the two electron pulses. (E) The traces show the measured spatial beam diameter versus the delay between the electron pulses for various numbers of electrons. The green traces are fits to Gaussian functions. Note the decrease in width with the decrease in the number N of electrons; here, N is relative (see text).