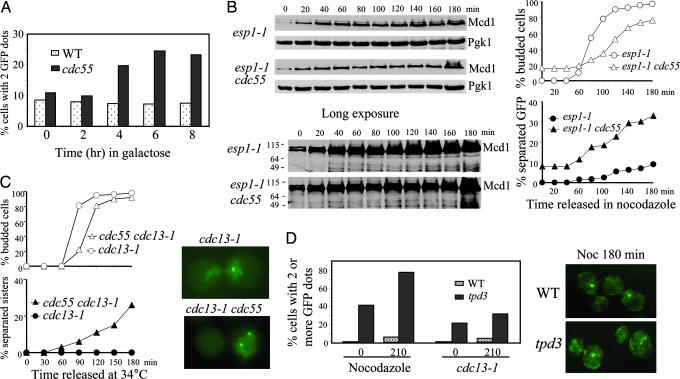
Fig. 2.
Δcdc55 cells exhibit precocious sister chromatid separation in the presence of Pds1. (A) Overexpression of Pds1 fails to suppress the premature separation of sister chromatids in Δcdc55 mutants. WT and Δcdc55 mutant cells carrying PGAL-PDS1-ΔDB were incubated in the presence of galactose and then collected every 2 h to examine sister chromatid separation. The percentage of cells with two or more GFP dots is shown. (B) Δcdc55 mutants exhibit separated sister chromatids when Esp1 is inactive. G1-arrested cells of esp1–1 and Δcdc55 esp1–1 carrying GFP-marked chromosome V and HA-tagged Mcd1 were released into YPD medium containing 20 μg/ml nocodazole and incubated at 37.5°C. The kinetics of sister chromosome separation and Mcd1 accumulation are shown. (C) Precocious sister chromatid separation in cdc13–1 Δcdc55. G1 cells of cdc13–1 and cdc13–1 Δcdc55 carrying URA3-GFP were released at 34°C. The cell-budding profile (Upper Left), kinetics of sister chromatid separation (Lower Left), and micrographs of cells with GFP dots (Right) are shown. (D) Nocodazole and cdc13–1-arrested Δtpd3 mutant cells display separated sister chromatids. WT and Δtpd3 mutant cells carrying URA3-GFP were synchronized at G1 and then released into medium containing 20 μg/ml nocodazole. Cells were collected at the indicated times to examine sister chromatid separation. Similar experiment was repeated with cdc13–1 and cdc13–1 Δtpd3 mutants released into YPD medium at 34°C. Percentages of cells with multiple GFP dots (Left) and fluorescence micrographs of cells incubated in nocodazole for 180 min (Right) are shown.