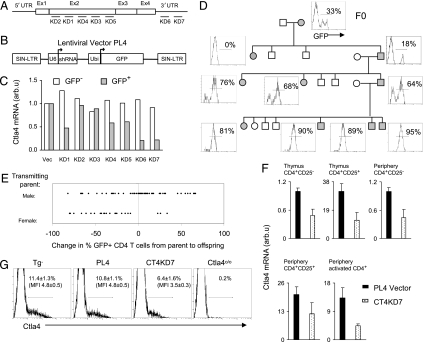
Fig. 1.
Generation of Ctla4 knockdown mice. (A) Diagram of the full-length Ctla4 mRNA and regions targeted by shRNA probes KD1–7. (B) The lentiviral vector used to express shRNA. Ubi, ubiquitin. (C) In vitro testing of the efficacy of the shRNA in silencing Ctla4 expression in activated T lymphocytes. Data are representative of two experiments. (D) Transmission of the Ctla4 KD7 (CT4KD7) lentigene and expression of the GFP reporter through generations. Filled and open symbols indicate, respectively, presence and absence of the lentigene. Histogram shows GFP expression by CD4+ peripheral blood cells. (E) Expression of the lentigene inherited from the male versus female parent. Data are pooled from two PL4 vector and two CT4KD7 lentigenic lines. Each dot represents one animal. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR assessment of Ctla4 mRNA in T cells from the thymus or periphery (spleen and lymph nodes) (mean ± SD). (G) Quantification of Ctla4 protein by intracellular flow cytometric staining of CD4+CD25+ lymph nodes cells ex vivo. Percentage of Ctla4+ population and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) are indicated (mean ± SD).