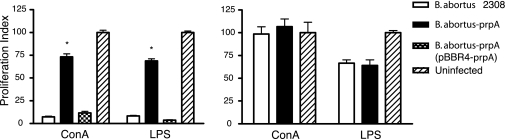
Fig. 3.
PrpA promotes a transient mice immunosuppressive status during Brucella infection. BALB/c mice were infected i.p. with B. abortus WT, B. abortus-prpA, and the complemented strain B. abortus-prpA (pBBR4-prpA). At 3 (Left) or 12 (Right) weeks after infection, spleens were removed, and splenocytes were treated for 72 h with ConA or E. coli LPS. Splenocyte proliferation was determined indirectly by [3H]thymidine incorporation. Bars represent the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations expressed as proliferation index, compared with the RPMI medium 1640-treated cells. At least three animals were used for each determination. ∗, Significant difference with uninfected or B. abortus-prpA (pBBR4-prpA)-infected mice stimulated with ConA and LPS (P < 0.01).