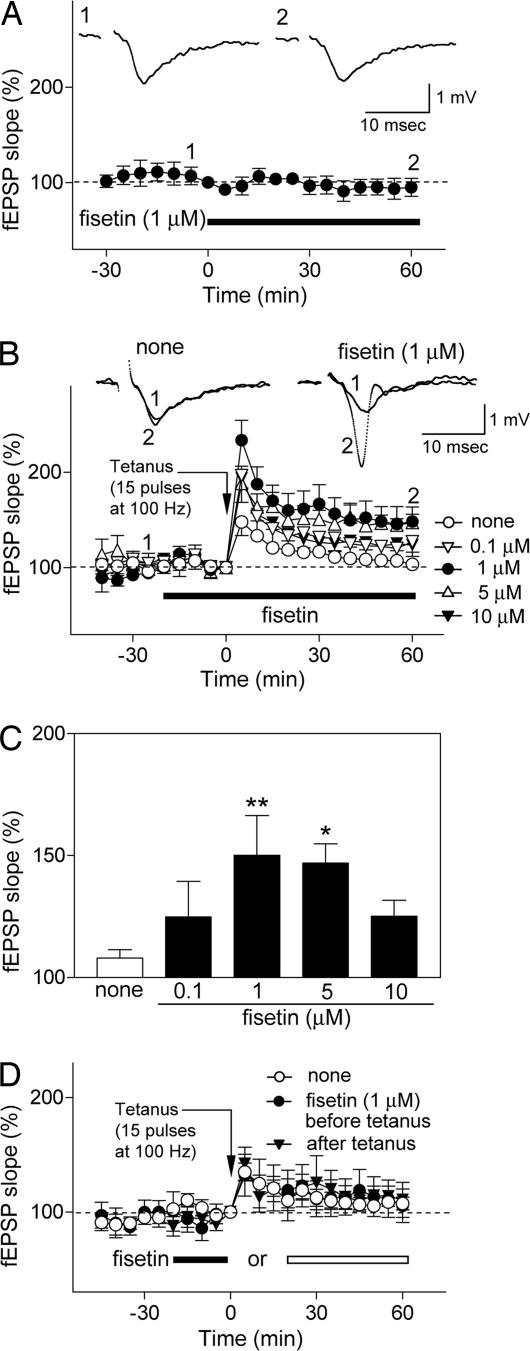
Fig. 3.
Fisetin facilitates the induction of LTP in Schaffer collateral CA1 pyrimidal cell synapses in rat hippocampal slices. (A) Effect of fisetin (1 μM, n= 6) on basal synaptic transmission. Hippocampal slices were exposed to fisetin during the time indicated by the black bar. The field excitatory postsynaptic potential (fEPSP) slope is expressed as the percentage of the value immediately before the addition of fisetin. (A Insets) Representative records 5 min before (Inset 1) and 60 min after (Inset 2) exposure to fisetin. Fisetin does not affect basal synaptic transmission. (B and C) Fisetin facilitates the induction of LTP after a weak tetanic stimulation (15 pulses at 100 Hz), which alone does not induce LTP in control slices. The effect of fisetin is dose-dependent. The hippocampal slices were untreated (n= 14) or exposed to fisetin (0.1 μM, n= 7; 1 μM, n= 8; 5 μM, n= 6; 10 μM, n= 6) for the time indicated by the black bar, and weak tetanic stimulation was applied at time 0. The fEPSP slope is expressed as the percentage of the value immediately before the application of weak tetanic stimulation. (B) Time course of changes in the fEPSP slope. (B Insets) Representative records at −25 min (Inset 1) and + 60 min (Inset 2) in control and 1 μM fisetin-treated slices. To compare the data among the groups, the averages of the fEPSP slopes 30–60 min after tetanic stimulation were calculated as an index of LTP magnitude; they are shown in C. (C) None: 108.0 ± 3.4%; 0.1 μM fisetin: 124.8 ± 14.6%, not significant vs. none; 1 μM fisetin: 150.1 ± 16.3%, **, P < 0.01 vs. none; 5 μM fisetin: 146.9 ± 7.9%, *, P < 0.05 vs. none; 10 μM fisetin: 150.1 ± 16.3%, ∗∗, P < 0.01 vs. none; 5 μM fisetin: 146.9 ± 7.9%, ∗, P < 0.05 vs. none; 10 μM fisetin: 125.2 ± 6.5%, not significant vs. none (ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test). All data are the mean ± SEM. (D) The facilitation of LTP by fisetin depends on the timing of its addition relative to the tetanic stimulus. Fisetin must be present during the stimulus to show facilitation of LTP. The hippocampal slices were untreated (n= 9) or exposed to 1 μM fisetin before (filled bar, n= 5) or after (open bar, n= 5) application of weak tetanic stimulation (15 pulses at 100 Hz). Data are presented as in B.